High-humidity Sensor of a New Trinuclear Ti3-Oxo
Cluster
SUN Shi-Hao, ZHANG Qian-Chong, YE Xiao-Liang, KASHI Chivanje evulu, LI Wen-Hua, WANG Guan-E* and XU Gang
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2203070-2203076 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3351
March 15, 2022
polyoxo-titanium clusters, semiconductor, chemiresistive sensor, humidity sensor
ABSTRACT
Crystalline
polyoxo-titanium clusters (PTCs), as a molecular model of TiO2 nanomaterials, have attracted
unprecedented attention due to their designable structure, tunable band gap, catalysis, and
photochromic properties. A new trinuclear Ti3-oxo cluster, [Ti3(μ2-O)(μ3-O)(abz)6(OiPr)2]·CH3CN·H2O (Ti3), was synthesized by solvothermal method with a yield of 60% by
using 4-aminobenzoic acid as ligand. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction shows
that it has a [Ti3(μ2-O)(μ3-O)(abz)6(OiPr)2]
trinuclear cluster structure. Ti3 crystallizes in monoclinic space group P21/c with a =
11.091(1), b = 22.837(2), c = 22.754(1) Å, β = 90.580(6)°, V = 5763.0(6) Å3, Z = 4, Dc = 1.345 g·cm-3, F(000) = 2412, μ = 2.743 mm−1, R =
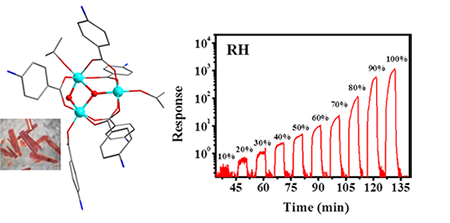
0.0796, and wR = 0.2260 (I > 2σ(I)). Ti3 shows typical semiconductive behavior determined by temperature-dependent conductivity
test. The chemiresistive humidity
sensor fabricated by Ti3 showed good
performance, including high response (four orders of magnitude current change
from 0 to 100% RH) and fast response time (160 s) and recovery time (26 s).