A New SERS Method Based on Shell-isolated Nanoparticles for Rapidly Quantitative Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide
WEN Bao-Ying, SHEN Tai-Long, WU Yuan-Fei and LI Jian-Feng*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 1604-1610 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3210
December 15, 2021
hydrogen peroxide, surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy, shell-isolated nanoparticles, ratiometric, glucose
ABSTRACT
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is an
important chemical substance produced in the metabolic process of organisms. Excess
or less production could lead to serious effects on the body. Therefore, the
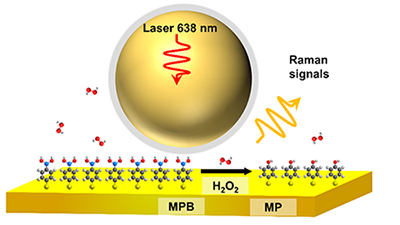
development of advanced technology to accurately detect the content of H2O2 is of great significance. Herein, we developed a new ratiometric SERS nanoprobe
based on shell-isolated nanoparticles (SHINs) for rapidly quantitative
detection of H2O2. Because of the small Raman
cross-section of H2O2, the ratiometric nanoprobe is an
effective method for indirect detection of H2O2, which is
designed based on the reaction of p-mercaptophenylboric
acid (MPB) with H2O2 to form p-mercaptophenol (MP). Meanwhile, the nanoprobe was used to achieve
quantitative detection of H2O2 and applied in
quantitative detection of actual sample¾glucose, whose linear correlation coefficient could
reach 0.9947 and 0.9812, respectively. This method expands the application of
SERS technology, especially provides a reference for the detection of molecules
with small Raman cross-section.