A Water-stable Tetranuclear Cd(II) Bicyclic Complex Used for the Picric Acid Detection
WANG Ming, WANG Xiao-Mei, CHEN Ming-Yu, LIU Cheng, DING Ge and ZHOU Xin-Hui*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 1461-1468 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3182
December 15, 2021
sensors, complex, picric acid, fluorescence
ABSTRACT
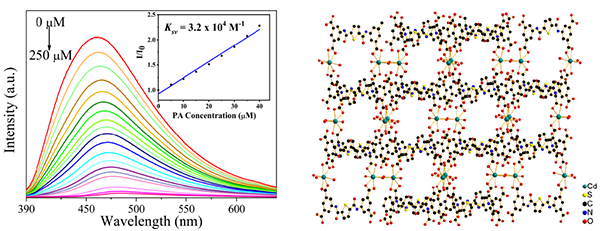
By solvothermal reaction of Cd(II) with organic ligand N,N΄-bis(3,5-dicarboxylphenyl)-thiophene-2,5- dicarboxamide (H4L), a water-stable complex [Cd4(H2L)4(H2O)10]·2CH3OH·8H2O·4DMF (1, C102H120Cd4N12O64S4) has been successfully synthetized (DMF = N,N-dimethylformamide). 1 crystallizes in the triclinic space group of P with a = 11.815(7), b = 16.209(9), c = 16.742(9) Å, α = 82.224(13)º, β = 76.741(13)º, γ = 70.313(12)º, V = 2932(3) Å3, Mr = 3115.93, Z = 1, F(000) = 1584, Dc = 1.765 Mg/cm3, µ = 0.901 mm−1, GOOF = 1.101, the final R = 0.0391 and wR = 0.1297 for 9007 observed reflections (I > 2s(I)). 1 is a tetranuclear Cd(II) bicyclic complex with strong ligand-based blue emission and can stably exist in aqueous solutions over the pH range of 2-11. 1 exhibits high sensitivity, selectivity and anti-interference capability for picric acid (PA) detection in aqueous solution by luminescent quenching. The value of quenching constant (Ksv) is 3.2 × 104 M-1 within the PA concentration range of 0~40 μM and the detection limit is 6.89 × 10-7 M. Lastly, we went into depth on possible mechanism of the luminescent quenching.