Theoretical Study on the Nitrogen-rich Derivatives Based on 1,2,4-Triazole and 1,2,3-Triazole Rings: an Extended Family of Power Performance Energetic Materials
JIA Jing-Xian, PANG Yu, YANG Jing*, LI Min-Xian, MENG Xiang-Jun, GAO Xiao-Zhen, LIU Li-Hua and LIU Meng-Na
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 1113-1121 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3143
September 15, 2021
4-nitro-5-(5-nitroimino-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)-2H-1,2,3-triazolate, high energy density materials, density functional theory, explosive
ABSTRACT
The geometric and electronic structures of the
derivatives of 4-nitro-5-(5-nitroimino-1,2,4-triazol-
3-yl)-2H-1,2,3-triazolate (named A~J) are explored employing density functional theory (DFT) calculations at
the B3LYP/6-311G** level of theory. Based on the optimized molecular
structures, the heats of formation (HOF) are obtained, and the electronic
properties, density and molecular sensitivity by characteristic heights (H50) are
discussed. Besides, the detonation performances (detonation velocity,
detonation pressure) are estimated via
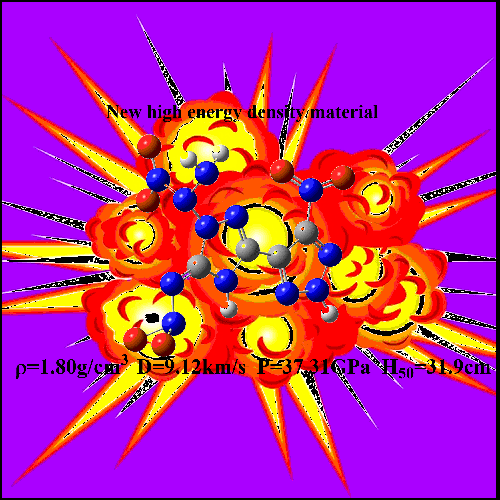
Kamlet-Jacobs (K-J) formula. Compounds B (H50 = 29.4
cm, ρ = 1.91 g/cm3, Q = 1563.04 cal/g, P = 36.05 GPa, D = 8.95 km/s) and H (H50 = 31.9
cm, ρ = 1.80 g/cm3, Q = 1610.09 cal/g, P = 37.31 GPa, D = 9.12 km/s) have positive HOFs
and remarkable insensitivity and good detonation performance, strongly
suggesting them as the acceptable new-type explosive. The initiating power
surpasses conventional primary explosives, such as HMX. The outstanding detonation power of
compounds B and H contributes to its future prospects as a
promising green primary explosive.