Cover Picture
Submit a Manuscript
Accurate design and synthesis of nonlinear optical crystals employing KBe2BO3F2 as structural template
Tao Ouyang, Yaoguo Shen*, Sangen Zhao
Tao Ouyang, Yaoguo Shen*, Sangen Zhao
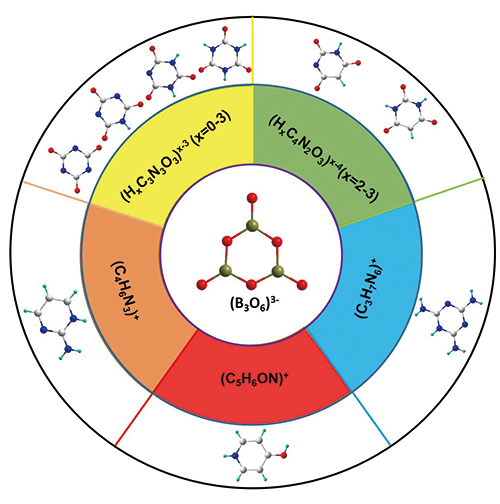
Compounds consisting of coplanar π-conjugated B3O6-typed structures: An emerging source of ultraviolet nonlinear optical materials
Lingli Wu, Huixin Fan, Chensheng Lin, Min Luo*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2023, 42: 100019 DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2023.100019
January 15, 2023
NLO crystals, B3O6-typed structures, π-conjugated, Anionic group theory
ABSTRACT
Nonlinear optical (NLO) materials as a crucial part of the laser science have attracted increasing attention from researchers because of their wide applications in information storages, modern science and technologies, et al. Based on the anionic group theory, the π-conjugated 6-membered rings (6-MRs), B3O6-typed structures have key contributions to the superior optical properties of β-Ba2B2O4 (β-BBO). In recent years, the organic coplanar π-conjugated B3O6-typed structures have caught researchers’ attention due to similar configurations to the (B3O6) groups, which are the potential sources for expending the (B3O6) groups with outstanding optical properties. Up to know, researchers have obtained many ultraviolet (UV) NLO crystals with excellent properties with π-conjugated B3O6-typed groups. Herein, these B3O6-typed groups could be divided into different categories according to the atoms constituting the 6-MRs: (HxC3N3O3)x−3 (x = 0–3) (cyanurate ion), (HxC4N2O3)x−4 (x = 2, 3) (barbiturate ion), (C3H7N6)+ (melamine ion), (C5H6ON)+ (4-hydroxypyridine cation), and (C4H6N3)+ (2-aminopyrimidinium cation). In this review, we introduced the research advances of NLO materials with π-conjugated B3O6-typed groups, and summarized the crystal structures, synthetic methods, optical performances, as well as the relationships between structures and properties. This work provided a clear perspective for understanding the coplanar π-conjugated B3O6-typed groups with their optical functional properties and promote the searches to develop potential NLO functional crystals.