Cover Picture
Structural insights into lithium-deficient type Li-rich layered oxide for high-performance cathode
Dongyu He, Wenxin Tong, Jia Zhang, Zhongyuan Huang, Ziwei Chen, Maolin Yang, Rui Wang, Wenguang Zhao, Zhewen Ma*, Yinguo Xiao* Submit a Manuscript
Structural insights into lithium-deficient type Li-rich layered oxide for high-performance cathode
Dongyu He, Wenxin Tong, Jia Zhang, Zhongyuan Huang, Ziwei Chen, Maolin Yang, Rui Wang, Wenguang Zhao, Zhewen Ma*, Yinguo Xiao* Submit a Manuscript
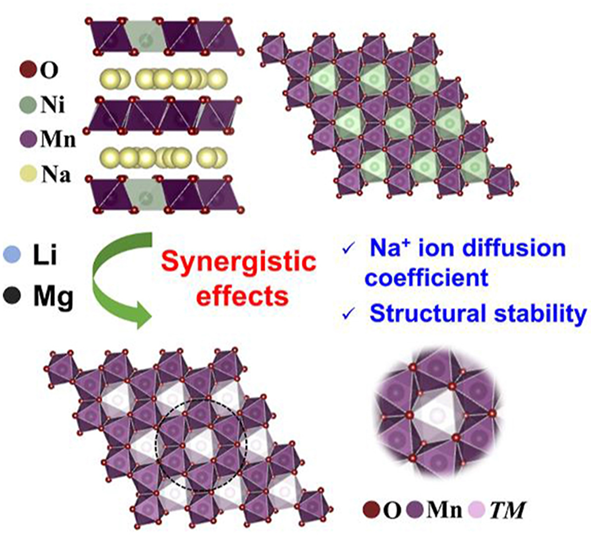
Alkali and alkaline ions co-substitution of P2 sodium layered oxides for sodium ion batteries
Yuncai Chen, Maolin Yang, Liangtao Yang, Ziwei Chen, Huiyun Li, Haw Jiunn Woo*, Shang-Sen Chi, Yinguo Xiao, Jun Wang*, Chaoyang Wang, Yonghong Deng*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2023, 42: 100028. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2023.100028
May 15, 2023
Sodium ions batteries; Sodium layered oxides; Alkali and alkaline elements co-substitution; Neutron diffraction; Structural evolution
ABSTRACT
Alkali and alkaline ion substitutions enhance the electrochemical properties of P2 sodium layered oxide, while the effect on electrochemical property enhancement of alkali and alkaline ions co-substitution is still unclear. In this work, the structural and electrochemical properties of the Li alkali and Mg alkaline ions co-substituted P2 layered oxide Na0.67(Li0.5Mg0.5)0.1(Ni0.33Mn0.67)0.9O2 are investigated in detail. Compared to the pristine and single-ion substituted materials, the co-substituted material shows an enhanced cycling performance with a reversible capacity of 127 mAh/g and a capacity retention of 75% over 100 cycles at 0.5C. Galvanostatic intermittent titration technique (GITT) and cyclic voltammetry (CV) results show that the Li and Mg synergistically improve the ion diffusion. Moreover, the structure stability is also improved by the Li and Mg co-substitution that is clarified by operando X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements. These results explain the origin of the enhanced electrochemical properties of the Li/Mg co-substituted P2 layered oxides for sodium ion batteries.