Cover Picture
UV-resistant salicylic acid as interface modifier for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells
Guo-Bin Xiao, Zihan Fang, Shengrong Yang*, Jing Cao*, Yu Tang* Submit a Manuscript
UV-resistant salicylic acid as interface modifier for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells
Guo-Bin Xiao, Zihan Fang, Shengrong Yang*, Jing Cao*, Yu Tang* Submit a Manuscript
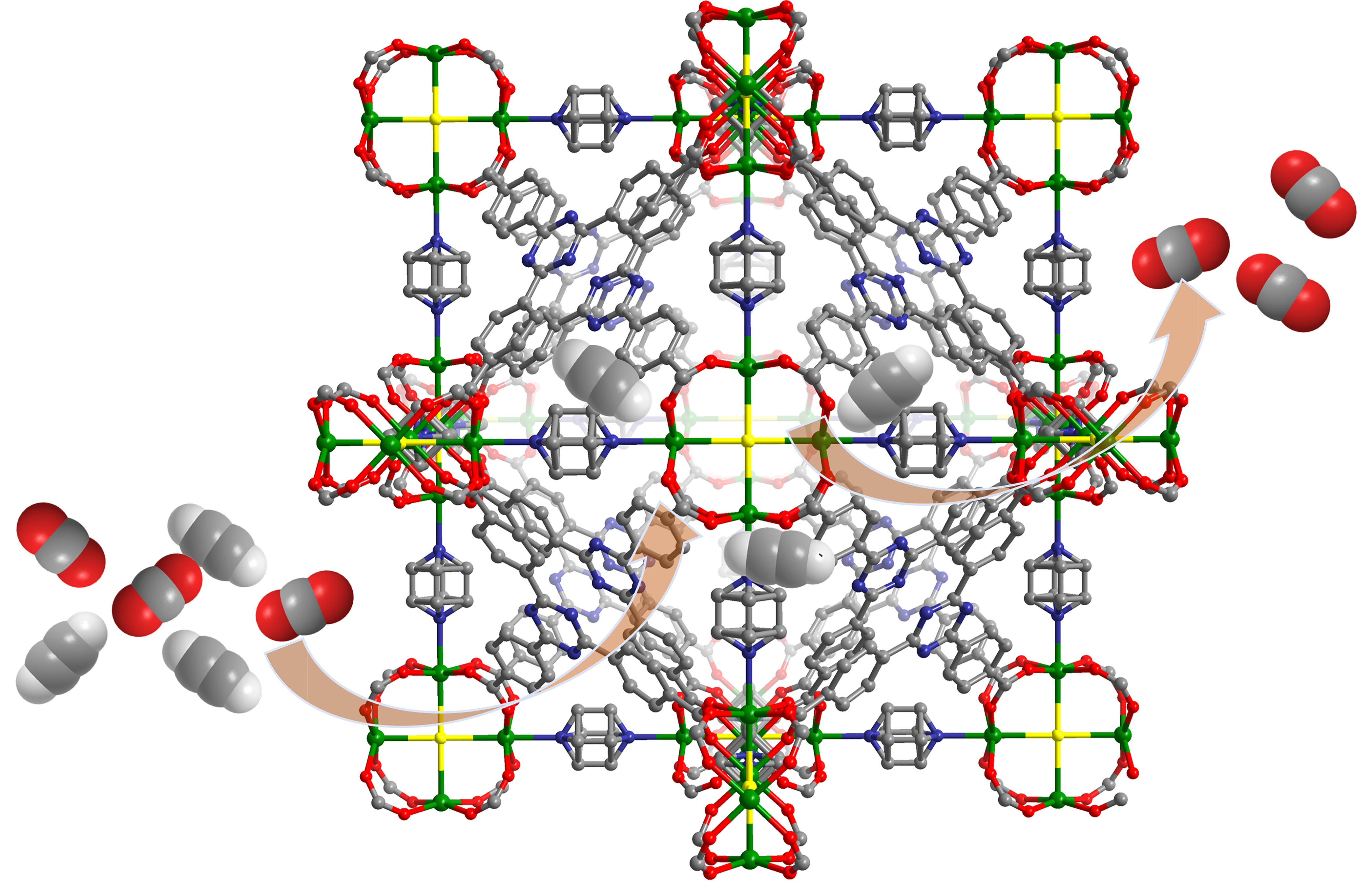
Auxiliary ligand-directed assembly of a non-interpenetrated cage-within-cage metal-organic framework for highly efficient C2H2/CO2 separation
Yong-Peng Li*, Jing-Jing Ni, Shu-Cong Fan, Quan-Guo Zhai*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2023, 42: 100070. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2023.100070
June 15, 2023
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs); Second auxiliary ligand; Acetylene storage; Acetylene/carbon dioxide separation
ABSTRACT
The development of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with highly efficient adsorption and separation of acetylene is very important and challenging in chemical industry due to the explosive nature of acetylene. Porous MOFs can be constructed by inserting a second auxiliary ligand, which allows the use of large ligands to construct non-interpenetrated structures and increase pore utilization. Herein, SNNU-205 is successfully synthesized, which connects two sets of interpenetrated structures to form a double walled cage-within-cage structure by using the introduction of a second auxiliary ligand. The modified pore environment enables SNNU-205 to efficiently selectively adsorb C2H2 over CO2. At 298 K and 1 atm, SNNU-205 can uptake much more C2H2 (76.3 cm3 g−1) than CO2 (47.3 cm3 g−1), resulting in a high substance ratio of C2H2-to-CO2 (1.6). More importantly, the ideal adsorbed solution theory selectivity calculations and column breakthrough tests further indicate SNNU-205 to be promising adsorbents for C2H2 adsorption and purification.