Electrostatically driven kinetic Inverse CO2/C2H2 separation in LTA-type zeolites
Yongheng Ren, Yang Chen, Hongwei Chen, Lu Zhang, Jiangfeng Yang, Qi Shi, Lin-Bing Sun, Jinping Li, Libo Li*
Submit a Manuscript
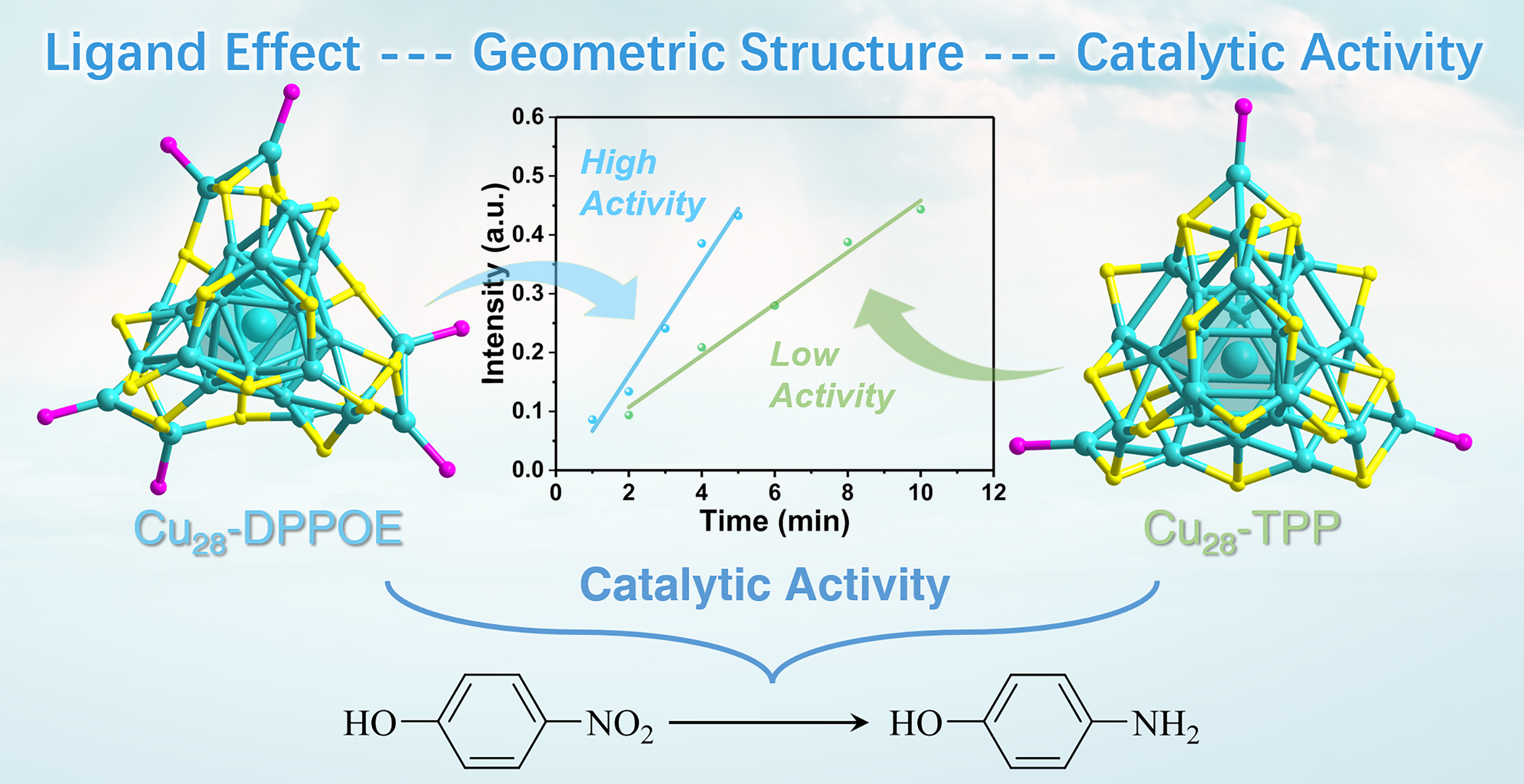
Luyao Lu, Chen Zhu, Fei Li, Pu Wang*, Xi Kang*, Yong Pei*, Manzhou Zhu*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2024, 43: 100411. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2024.100411
October 15, 2024
Atomically precise nanoclusters; Copper nanoclusters; Ligand effect; Structure-property correlation; Catalytic hydrogenation
ABSTRACT
The ligand effects have been extensively investigated in Au and Ag nanoclusters, while corresponding research efforts focusing on Cu nanoclusters remain relatively insufficient. Such a scarcity could primarily be attributed to the inherent instability of Cu nanoclusters relative to their Au/Ag analogues. In this work, we report the controllable preparation and structural determination of a hydride-containing Cu28 nanocluster with a chemical formula of Cu28H10(SPhpOMe)18(DPPOE)3. The combination of Cu28H10(SPhpOMe)18(DPPOE)3 and previously reported Cu28H10(SPhoMe)18(TPP)3 constructs a structure-correlated cluster pair with comparable structures and properties. Accordingly, the ligand effects in directing the geometric structures and physicochemical properties (including optical absorptions and catalytic activities towards the selected hydrogenation) of copper nanoclusters were analyzed. Overall, this work presents a structure-correlated Cu28 pair that enables the atomic-level understanding of ligand effects on the structures and properties of metal nanoclusters.