Cover Picture
Hydrogen spillover enhances the selective hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes on the Cu–O–Ce interface
Jinyuan Cui, Tingting Yang, Teng Xu, Jin Lin, Kunlong Liu*, Pengxin Liu* Submit a Manuscript
Hydrogen spillover enhances the selective hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes on the Cu–O–Ce interface
Jinyuan Cui, Tingting Yang, Teng Xu, Jin Lin, Kunlong Liu*, Pengxin Liu* Submit a Manuscript
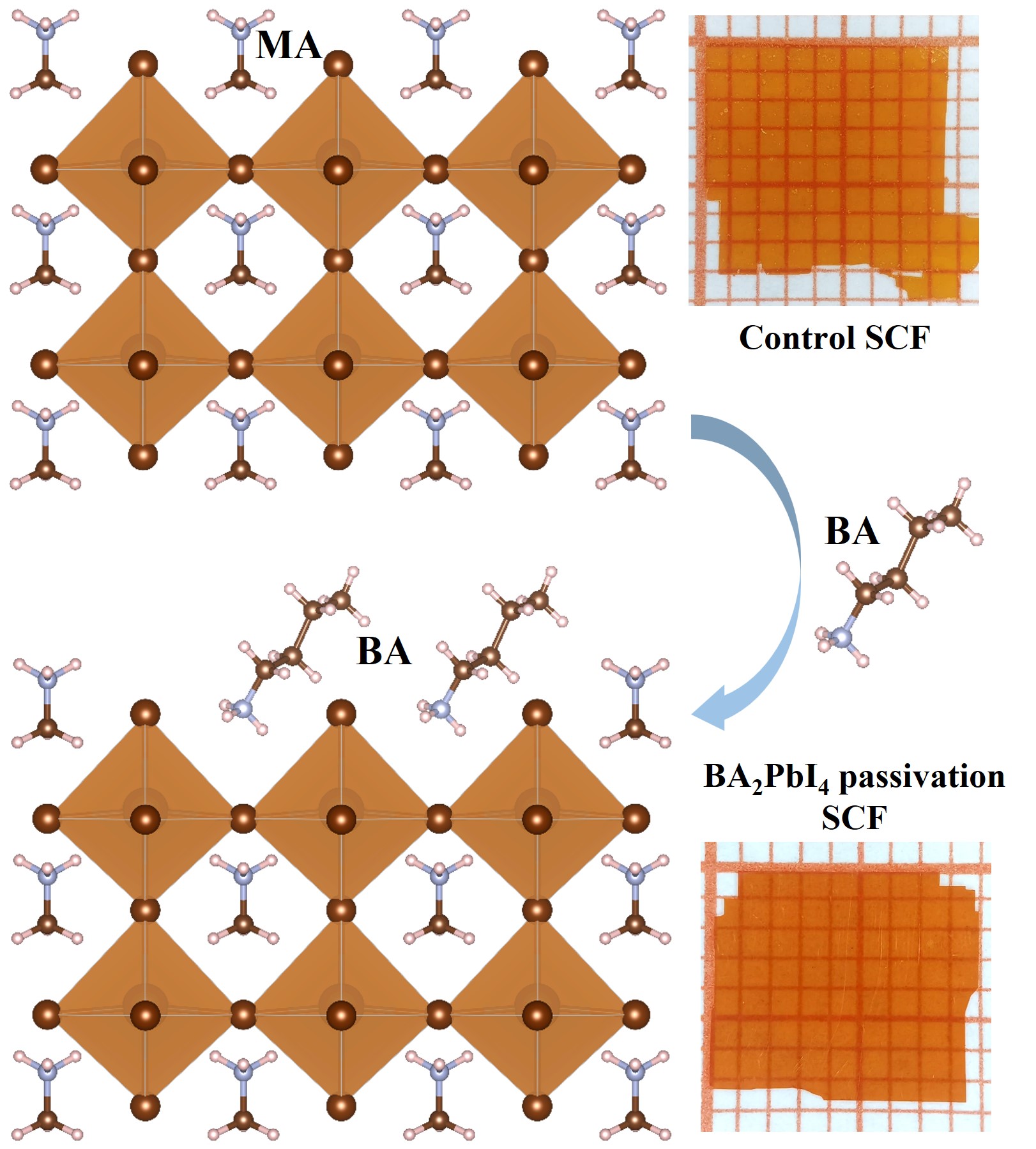
In-situ passivating surface defects of ultra-thin MAPbBr3 perovskite single crystal films for high performance photodetectors
Wenli Xu, Yingzhao Zhang, Rui Wang, Chenyang Liu, Jialin Liu, Xiangyu Huo, Xinying Liu, He Zhang, Jianxu Ding*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2025, 44(1), 100454. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2024.100454
January 1, 2025
Perovskite; Single crystal films; Space confined method; Surface passivation; Photodetectors
ABSTRACT
Ultra-thin single crystal film (SCF) without grain boundary inherits low charge recombination probability as bulk single crystals. However, its low depth brings a high surface defect ratio and hinders the carrier transport and extraction, which affects the performance and stability of optoelectronic devices such as photodetectors, and thus surface defect passivation is of great practical significance. In this paper, we use the space confined method to grow MAPbBr3 SCF and selected BA2PbI4 for surface defect passivation. The results reveal that BA cation passivates MA vacancy surface defects, reduces carrier recombination, and enhances carrier lifetime. The carrier mobility is as high as 33.6 cm2 V−1 s−1, and the surface defect density is reduced to 3.4 × 1012 cm−3. Therefore, the self-driven vertical MAPbBr3 SCF photodetector after surface passivation exhibits more excellent optoelectronic performance.