Alkyl-linked TiO2@COF heterostructure facilitating photocatalytic CO2 reduction by targeted electron transport
Jiangqi Ning, Junhan Huang, Yuhang Liu, Yanlei Chen, Qing Niu, Qingqing Lin, Yajun He, Zheyuan Liu, Yan Yu, Liuyi Li* Submit a Manuscript
Jiaqi Ma, Lan Li, Yiming Zhang, Jinjie Qian, Xusheng Wang*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2024, 43: 100466. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2024.100466
December 15, 2024
Covalent organic frameworks; Photocatalysis; Photocatalytic CO2 reduction; Characterizations; Structures
ABSTRACT
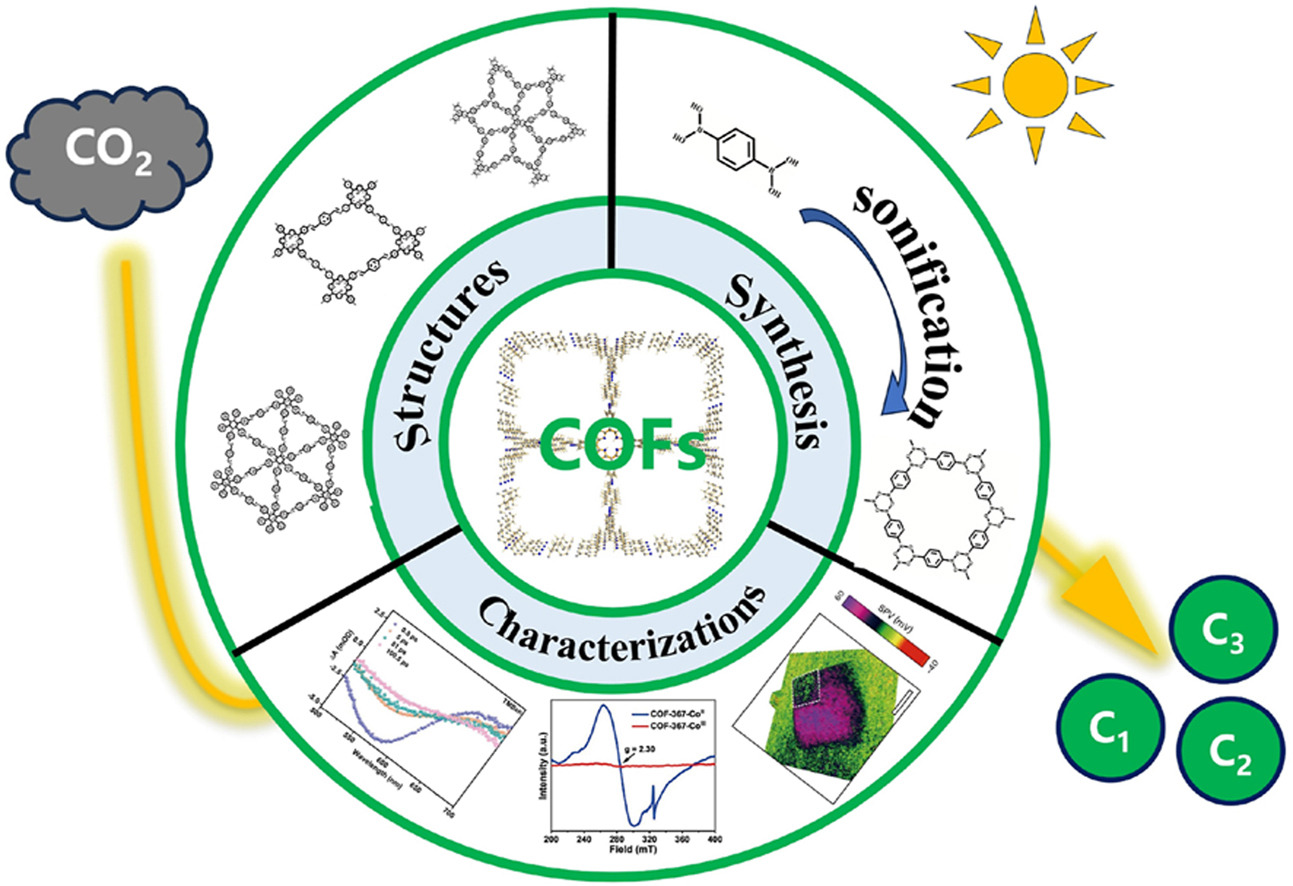
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are a class of stable two- or three-dimensional porous materials which are composed of ordered organic units connected by strong covalent bonds. Owing to their outstanding physical and chemical properties, COFs have garnered significant attention in recent years as promising candidates for photocatalytic reduction of CO2. In this review, we will first summarize the synthesis and structures of COFs, then provide an overview of characterization techniques used for COFs, and finally systematically review recent research progress on the photocatalytic reduction of CO2 using COFs. Fully understanding of the relations between COFs structures and photocatalytic CO2 reduction would greatly enhance the further development of this emerging area. Herein we address this gap, aiming not only to provide the latest research progress of COFs materials in the photocatalytic reduction of CO2 but also to summarize the advanced characterizations for COFs structures and illustrate how the structures guide the photocatalytic reduction of CO2 performance.