Cover Picture
Hierarchical Pt/NiO hollow nanofibers for catalytic oxidation of HCHO at room temperature
Xinyu Zeng, Zhuofan Zeng, Qingqing Hu, Kejun Liu, Lei Ming, Bei Cheng, Wang Wang*, Guoqiang Luo, Shaowen Cao* Submit a Manuscript
Hierarchical Pt/NiO hollow nanofibers for catalytic oxidation of HCHO at room temperature
Xinyu Zeng, Zhuofan Zeng, Qingqing Hu, Kejun Liu, Lei Ming, Bei Cheng, Wang Wang*, Guoqiang Luo, Shaowen Cao* Submit a Manuscript
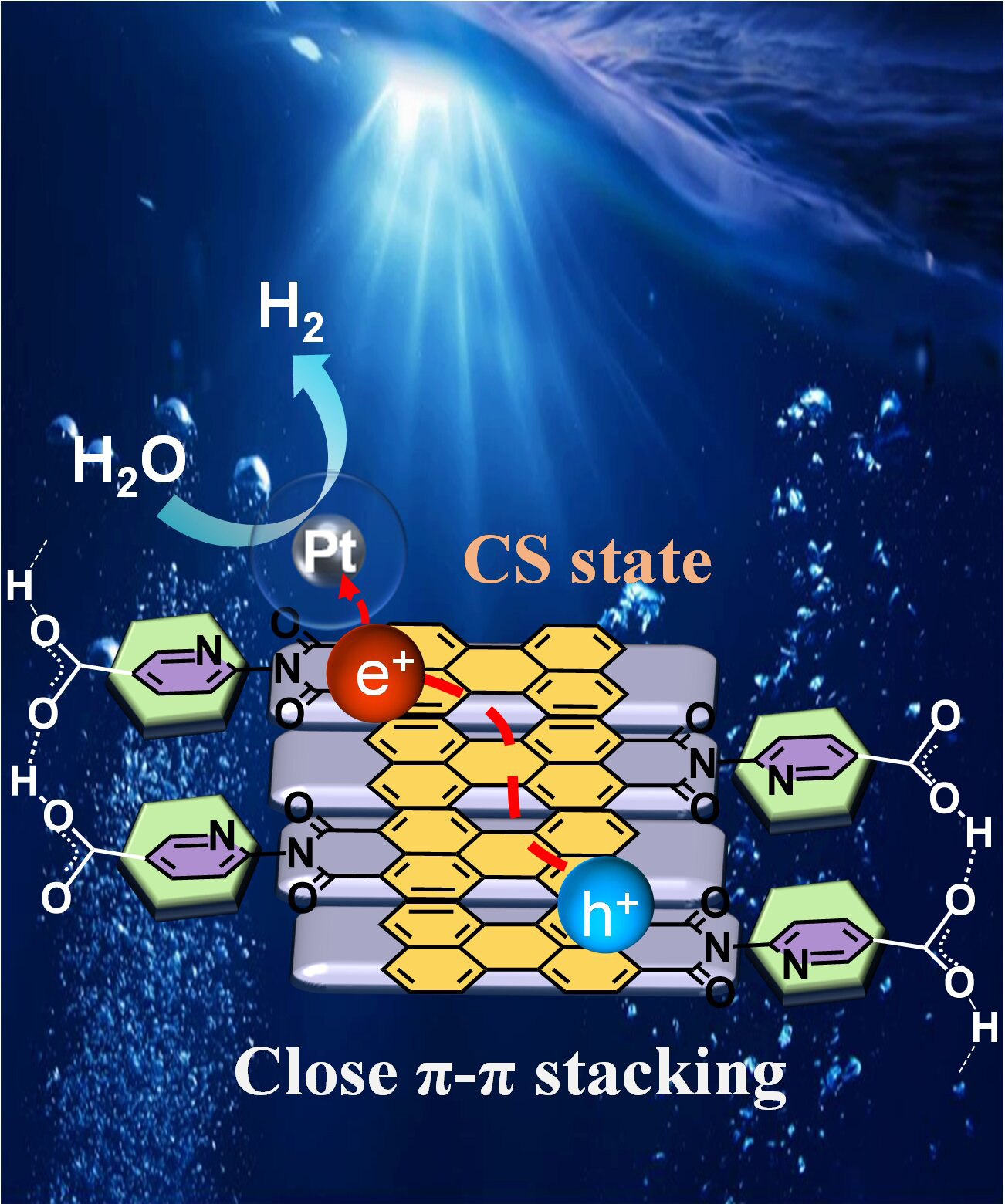
Close π-π stacking facilitated intermolecular charge separation in self-assembled perylene monoimide for photocatalytic hydrogen production
Shuhong Wu, Wanying Han, Ying Wang*, Yan Zhuang, Hui Niu, Lurong Li, Junhui Wang, Yuan Liu, Huan Lin, Kaifeng Wu, Jinni Shen, Yingguang Zhang*, Michael K.H. Leung, Jinlin Long
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2025, 44(6), 100592. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2025.100592
June 1, 2025
Photocatalysis; Hydrogen evolution; Supramolecular semiconductor; Perylene monoimide; π-π stacking
ABSTRACT
The tightness of π-π stacking in supramolecular organic semiconductors plays a crucial role in governing the spatial separation and migration dynamics of photogenerated charge carriers, ultimately determining their photocatalytic performance. To achieve close π-π stacking, the suitable design of molecular structure is essential. Therefore, two isomers of pyridine carboxylic acid-modified perylene monoimide (PMI) were designed and synthesized, namely PM5A and PM6A. In aqueous solution, these molecules self-assemble into aggregates, which exhibit distinct stacking properties and optical characteristics. Upon photoexcitation, the loose π-π stacking of PM5A favors the generation of charge-transfer excitons (CTEs) over charge-separation excitons (CSEs). In contrast, PM6A, stabilized by intermolecular hydrogen bonds and possessing close π-π stacking, undergoes efficient charge separation (CS) to produce CSEs within 4.5 picoseconds. When incorporated into metal-insulator-semiconductor (MIS) photosystems with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)-capped Pt, the Pt/PVP/PM6A system demonstrates a hydrogen evolution rate (HER) of 8100 μmol g−1 h−1, nearly five times higher than that of the Pt/PVP/PM5A system. Additionally, the maximum apparent quantum efficiency (AQE) reaches approximately 2.1% under irradiation with light of a single wavelength of λ = 425 nm.