Self-organized TiO2 Nanotube Arrays with Controllable
Geometric Parameters for Highly Efficient PEC Water Splitting
WANG Tian-Ming, CHEN Yan-Xin*, TONG Mei-Hong, LIN Shi-Wei, ZHOU Jing-Wen, JIANG Xia and LU Can-Zhong*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2202159-2202167 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3280
February 15, 2022
photoelectrochemistry, water-splitting, TiO2 nanotube arrays, H2
ABSTRACT
In this report, a series of self-organized TiO2 nanotube arrays were prepared by anodization of titanium foil in mixed
electrolytes composed of water, ethylene glycol, and NH4F. Their photoelectrochemical (PEC)
performance as a photoanode was characterized by the PEC water-splitting
hydrogen (H2) generation reaction. The internal relationship between
the TiO2 nanotube arrays (TNTAs) morphology and their PEC
performance was thoroughly investigated. Our results show that when the etching
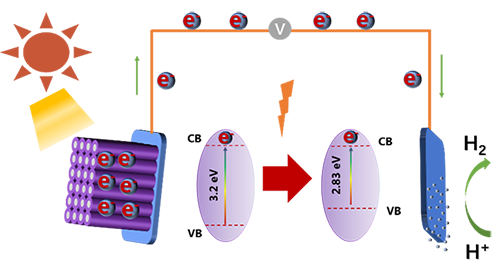
time is 10 hours, the length of the as-prepared TNTAs is about 20.78 μm and the measured photocurrent density
is around 1.25 mA·cm-2 with applied bias voltage 0.6 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) under simulated sunlight irradiation, which is 976
times higher than that of the TiO2 substrate without nanotubes
architecture (0.00128 mA×cm-2). More interestingly, the results of
the IPCE measurement show that the band-gap of the as-prepared TNTAs is reduced
from 3.20 to 2.83 eV. The corresponding optical response limit is also extended
from 400 nm to TiO2 nanotube arrays is 510 nm, which indicates that
the increasement of the TNTAs PEC performance benefits from the great
improvement of its utilization of both the UV and visible light irradiation.