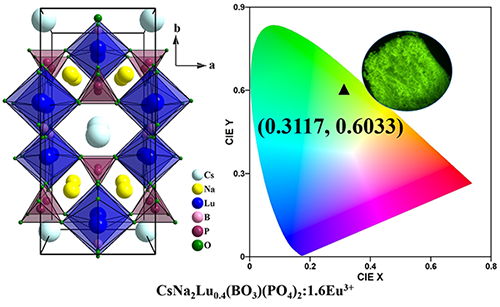
A New Borate-phosphate Compound CsNa2Lu2(BO3)(PO4)2: Crystal Structure and Tb3+ Doped Luminescence
SHI Jian-Chao, WANG Hao*, ZHANG Rui-Juan and ZHAO Dan*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2202141-2202147 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3284
February 15, 2022
borate-phosphate, crystal structure, photoluminescence, Tb3+
ABSTRACT
Composite borate-phosphate compounds have always
attracted much attention for their structure diversity and interesting
properties. In this work, a new borate-phosphate CsNa2Lu2(BO3)(PO4)2 (CNLBP) was found for the first time and its structure was characterized by
single-crystal X-ray diffraction method. It crystallizes in orthorhombic
system, space group Cmcm with a = 6.8750(5), b = 14.6919(1), c =
10.5581(7) Å, V = 1066.44(1) Å3, Z = 4, Mr = 777.58, Dc = 4.843 g/cm3, F(000) =
1368, μ(MoKα) = 22.20 mm-1, R(F2 > 2σ(F2)) =
0.0173 and wR(F2) = 0.0367. The structure of
CNLBP features a chain framework of [Lu2(BO3)(PO4)2]∞ that delimits 1D tunnels filled by Na+ and Cs+ ions. Phosphors CNLBP:xTb (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2,
0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0) were prepared, and it can emit bright green light under
near-UV excitation due to the 5D4→7Fj (j = 6, 5, 4, 3) transition of Tb3+. Due to the large separation of
Lu3+ ions in CNLBP structure lattice, the optimal concentration of
Tb3+ is 80%, and concentration quenching occurs only for the full Tb3+ concentration.