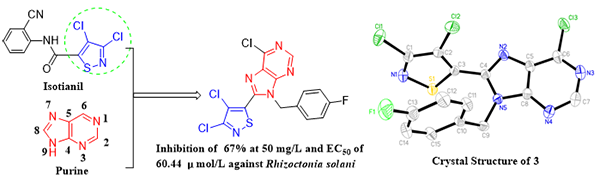
Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Fungicidal Activity of 3,4-Dichloro-5-(6-chloro-9-(4-fluorobenzyl)- 9H-purin-8-yl)isothiazole
WANG Wei-Bo, LIU Xiao-Yu, LI Zhi-Xinyi, GAO Wei, LV You, LI Kun, GLUKHAREVA Tatiana V.*, TANG Liang-Fu and FAN Zhi-Jin*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2202091-2202097 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3235
February 15, 2022
purine, synthesis, crystal structure, fungicidal activity
ABSTRACT
3,4-Dichloro-5-(6-chloro-9-(4-fluorobenzyl)-9H-purin-8-yl)isothiazole, a novel purine
derivative, was synthesized by the cyclization of pyrimidine amine. Its
structure was characterized by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, 19F
NMR, H RMS and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. This compound 3 is crystallized from a mixed solvent
of dichloromethane and n-hexane (1:2,
v/v) for structural identification as monoclinic crystal system, space group P21/n with a = 11.66250(10), b = 8.21300(10), c = 17.77920(10) Å, V = 1676.34(3) Å3, Z = 4, Dc = 1.643
g/cm3, F(000) = 832.0 and μ = 6.301 mm-1. 22315
reflections were measured (8.43≤2θ≤158.10°), of which 3532 were unique (Rint = 0.0311) and used in all calculations. The final R = 0.0334 (I > 2σ(I))
and wR = 0.0842 (reflections). The title
compound showed over 50% of growth inhibition against Botrytis cinereal, Cercospora
arachidicola, Gibberella zeae, Rhizoctonia solani and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum at 50 mg/L, and
its EC50 value against R. solani was 60.44 µmol/L, which was active at the same level as that
of positive control diflumetorim
with its EC50 value of 60.29 µmol/L and less active than YZK-C22 with its EC50 value
of 12.32 µmol/L, respectively. Our studies discovered that the combination of bioactive substructures
of isothiazole with purine could be an
effective way to novel fungicide development.