Structure and Properties of a Cd(II) Metal-organic Framework Based on a Newly Designed Heterotopic Tripodal N-Donor Ligand
HUANG Jie-Fen, CHEN Yi-Hao, LIANG Zhen-Hua, ZHENG Sheng-Run* and CAO Jun*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2202073-2202078 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3274
February 15, 2022
heterotopic tripodal ligand, metal-organic framework, topology, crystal structure
ABSTRACT
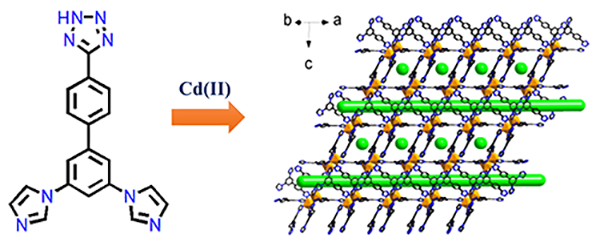
In this paper, a Cd(II)
metal-organic framework (MOF), Cd-DIBT (HDIBT = 5-(3΄,5΄-di(1H-
imidazol-1-yl)-[1,1΄-biphenyl]-4-yl)-1H-tetrazole), has been constructed based on a newly designed heterotopic tripodal
ligand containing both imidazolyl and pyrazolyl groups.
The Cd-DIBT exhibits a new three-dimensional (3,3,9)-connected trinodal network topology with point
symbol of (42·6)(43)2(48·615·812·10) (namely scnu)
based on binuclear secondary building blocks (SBUs). Staggered 1D channels were
observed in such framework and was estimated to have 5487 Å3 potential solvent area (56%). The stability study reveals that the framework is
unstable and easily transforms into amorphous MOF after the removal of guest
molecules. In addition, the Cd-DIBT shows a ligand-centered luminescence.