Synthesis, Crystal Structure and DNA-Binding Property of a New Cu(II) Complex Based on 4-(Trifluoro-methyl)nicotinic Acid
SHAN Feng-Lin, SONG Huan, GAO Xue-Zhi, LI Bing and MA Xiao-Xia*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2202057-2202063 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3257
February 15, 2022
4-(trifluoro-methyl) nicotinic acid, crystal structure, DNA
ABSTRACT
A
new complex [Cu1.5(tfc)3(H2O)4]·3H2O (1, Htfc =
4-(trifluoro-methyl) nicotinic acid) has been synthesized and characterized by X-ray
single-crystal diffraction,
elemental analysis, IR spectra and thermo-gravimetric
analysis. 1 belongs to orthorhombic system, space group Pccn with a = 44.507(2), b = 10.7710(6), c = 11.7544(7)
Å, V = 5634.9(6) Å3, Z = 1, Dc =
1.803 mg·cm-3, F(000) = 3068, μ = 1.266 mm-1,
the final R = 0.0488 and wR = 0.1103 with I > 2σ(I). The Cu(II) ion is
coordinated by two N and two O atoms from different Htfc as well as two O atoms
from two coordinated water molecules, forming a 0D motif with distorted
octahedral geometry. The adjacent 0D units
are linked into 2D structures through bridge connection coordination mode. In
addition, the binding properties of
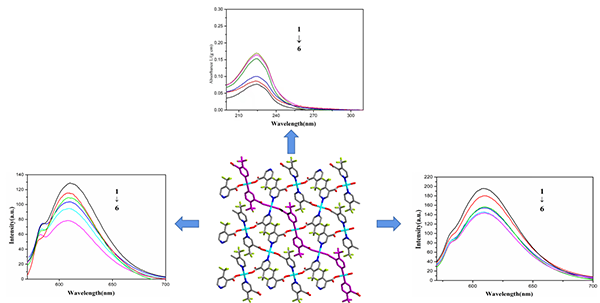
the complex with CT-DNA were investigated by fluorescence and ultraviolet spectra.
UV spectra indicate classical intercalation between the complex
and CT-DNA. Moreover, the interactions between the ligand and the complex with
CT-DNA were studied by EtBr fluorescence probe, which proved that these
compounds bind to CT-DNA through an intercalation mode. The binding constants
were 0.76 and 1.15 for Htfc and complex 1,
which means 1 has stronger interaction with CT-DNA than Htfc.