Effect of Fluorination on the Crystal Structure, Stability and Gas Adsorption Property in Zinc(II) Metal-organic Frameworks
ZHANG Xin, CHEN Zhen-Xia, YANG Yong-Tai, DENG Ming-Li* and WENG Lin-Hong
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2202049-2202056 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3264
February 15, 2022
metal-organic frameworks, fluorine functionalization, X-ray crystallography, gas adsorption
ABSTRACT
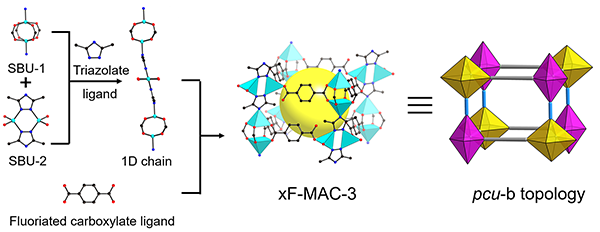
Three zinc(II) metal-organic
frameworks (xF-MAC-3) have been synthesized by using Zn(II) salts,
3,5-dimethyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole (Hdmtrz) and different fluorination
degree carboxylate ligands, which are analogic structures and can be described
as (6,6)-connected pcu-b net. We find that the fluorine atoms have
structural regulation effect on xF-MAC-3, which can not only enlarge the
torsion angle 𝜑 of carboxylate ligands but
also elevate the space group of structures. Besides, the CO2-273 K uptake increased from 23.21 cm3·g-1 (MAC-3) to 36.13 cm3·g-1 (4F-MAC-3) and H2-77
K uptake increased from 24.33 cm3·g-1 (MAC-3) to
59.79 cm3·g-1 (4F-MAC-3), which means fluorination
can enhance the gas adsorption uptake of xF-MAC-3 analogues. Furthermore, the results of fluorination in xF-MAC-3 analogues offer a potential way to study the ligand pre-functionalization
effect on the structures and properties of MOFs analogues.