CoMFA Study on Anti-proliferative Activity of Fluoroquinolone Amide Derivatives
FENG Hui, CAO Jing-Pei* and FENG Chang-Jun*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2203241-2203247 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3343
March 15, 2022
fluoroquinolone amide derivatives, Hep-3B cell, Capan-1cell, HL60 cell, anti-proliferative activity, comparative molecular field analysis
ABSTRACT
The in vitro
anti-proliferative activity (pICi, i = hp, ca, hl)
of fluoroquinolone (rhodanine α,β-unsaturated ketone) amide
compounds, referred to as “fluoroquinolone amide derivatives (FQADs)” towards Hep-3B,
Capan-1 and HL60 cells, was studied by the 3D-QSAR method of comparative molecular
field analysis (CoMFA). Based on the training set of 14 compounds, the
prediction model was established, which was further verified by the test set of
5 compounds with template molecule included. It is found that steric and
electrostatic fields contribute 66.8%
and 33.2% to pIChp,
61.4% and 38.6% to pICca, and 61.5% and 38.5% to pIChl,
respectively. The Rcv2 (i.e,
cross-validation coefficient) is 0.324, 0.381, and 0.421 for pIChp, pICca,
and pIChl, respectively, while the
corresponding R2 (i.e, non-cross-validation
coefficient) all reach 0.999. Then, the models were employed to estimate the
activities of the training and test compounds, and the results show that the
stability and predictability of developed models are very satisfactory.
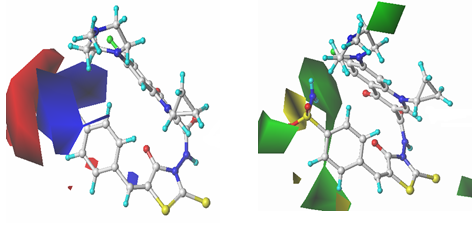
According to the contour maps of steric and electronic fields, bulky groups
linked to 2-, 3-, 4-positions of phenyl ring, and electropositive groups near the
4-position and electronegative groups far away may increase the
anti-proliferative activity. Using the information provided by the 3D contour maps, four new FQADs owing higher anti- proliferative activity were designed, but
their effectiveness should be further tested by experiments.