Discovery of Benzimidazole Derivatives as Novel Aldosterone Synthase Inhibitors: QSAR, Docking Studies, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation
GUO Hong-Mei, YU Na, FU Le, LI Guang-Ping, SHU Mao and LIN Zhi-Hua*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2203193-2203210 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3321
March 15, 2022
hypertension, 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation, CYP11B2 inhibitors
ABSTRACT
Aldosterone synthase inhibitors can lessen the
production of aldosterone in organisms, which effectively affecting the
treatment of hypertension. A series of computational approaches like QSAR,
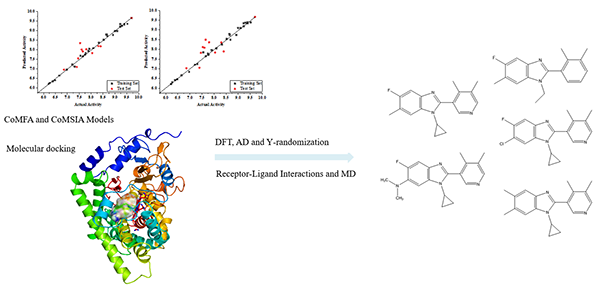
docking, DFT and molecular dynamics simulation are applied on 40 benzimidazole
derivatives of aldosterone synthase (CYP11B2) inhibitors. Statistical
parameters: Q2 = 0.877, R2 = 0.983 (CoMFA)
and Q2 = 0.848, R2 = 0.994 (CoMSIA)
indicate on good predictive power of both models and DFT’s result illustrates
the stability of both models. Besides, Y-randomization test is also performed
to ensure the robustness of the obtained 3D-QSAR models. Docking studies
show inhibitors rely on π-π interaction with residues, such as
Phe130, Ala313 and Phe481. Molecular dynamics simulation results further
confirm that the hydrophobic interaction with proteins enhances the inhibitor’s
inhibitory effect. Based on QSAR studies and molecular docking, we designed
novel compounds with enhanced activity against aldosterone synthase.
Furthermore, the newly designed compounds are analyzed for their ADMET
properties and drug likeness and the results show that they all have excellent
bioavailability.