QSAR Models for Predicting Additive and Synergistic Toxicities of Binary Pesticide Mixtures on Scenedesmus Obliquus
MO Ling-Yun, YUAN Bai-Kang, ZHU Jie, QIN Li-Tang* and DAI Jun-Feng*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2203166-2203177 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3306
March 15, 2022
pesticide, QSAR, toxicity prediction, binary mixture, algae
ABSTRACT
Pesticides
released into the environment may pose potential risks to the ecological system
and human health. However, existing toxicity data on pesticide mixtures still
lack, especially regarding the toxic interactions of their mixtures. This study
aimed to determine the toxic interactions of binary mixtures of pesticides on Scenedesmus
Obliquus (S. obliquus) and to build quantitative structure-activity
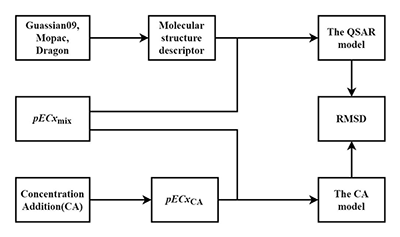
relationship models (QASR) for predicting the mixture toxicities. By applying
direct equipartition ray method to design binary mixtures of five pesticides (linuron,
dimethoate, dichlorvos, trichlorfon and metribuzin), the toxicity of a single
pesticide and its mixture was tested by microplate toxicity analysis on S.
obliquus. The QASR models were built for combined toxicity of binary
mixtures of pesticides at the half-maximal effective concentration (EC50),
30% maximal effective concentration (EC30) and 10% maximal
effective concentration (EC10). The results showed that the single
toxicity follows: metribuzin > linuron > dichlorvos > trichlorfon > dimethoate.
The mixtures of linuron and trichlorfon, dichlorvos
and metribuzin, dimethoate and metribuzin induced synergetic effects, while the
remaining binary mixtures exhibited additive. The
developed QSAR models were internally validated using the leave-one-out
cross-validation (LOO), leave-many-out cross-validation (LMO), bootstrapping,
and y-randomization test, and externally validated by the test sets. All three QSAR models satisfied well with the
experimental values for all mixture toxicities, and presented high internally (R2 and Q2 > 0.85) and externally (Q2F1, Q2F2, and Q2F3 >
0.80) predictive powers. The developed QSAR models
could accurately predict the toxicity values of EC50, EC30 and EC10 and were superior to the concentration addition
model's results (CA). Compared to the additive effect, the QSAR model could
more accurately predict the binary mixture toxicities of pesticides with
synergistic effects.