In-situ Growth of Carbon Nanosheets Intercalated with TiO2 for Improving Electrochemical Performance and Stability of Lithium-ion Batteries
HU Yan-Jie, YIN Yan-Hong*, ZHANG Ming, WU Zi-Ping* and SHEN Zhong-Rong*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 1513-1524 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3189
December 15, 2021
carbon nanosheets, TiO2, in situ growth, template, storage lithium
ABSTRACT
In
situ growth of carbon nanomaterials on active substance is a very favorable strategy
for the preparation of electrode in lithium-ion batteries with excellent electrochemical
performance and high stability. Small-sized
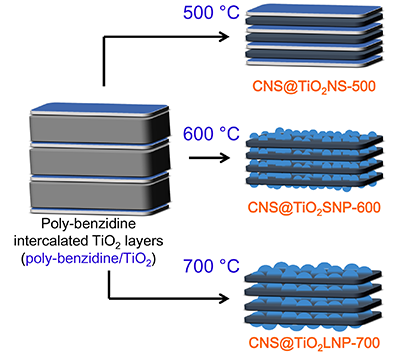
TiO2 nanoparticles intercalated into carbon nanosheets (CNS@TiO2SNP-600)
were successfully synthesized via in-situ polymerization-carbonization method, utilizing layered H2Ti4O9 (HTO) as template and benzidine as carbon source. The morphology and
size of TiO2 are greatly influenced by carbonization temperature. The coin cell with the CNS@TiO2SNP-600
electrode demonstrates a discharge specific capacity of 430.4 mAh×g-1 at a current density of 0.1 A×g-1, and the capacity retention rate is
88.1% after 100 cycles; and it also displays a high discharge specific capacity
of 101.8 mAh×g-1 at a high current density of 12.8 A×g-1. The excellent electrochemical
performances can be ascribed to the capacitance effect originated from the
intercalated structure of in-situ grown CNS and TiO2 nanoparticles. We believe
this type of materials can be widely used in the lithium-ion batteries and
other related green chemical fields.