Enhanced Upconversion Emissions of TiO2:Yb3+/Tm3+ Nanocrystals: Comparison with Different Effects of Li+, Mn2+ and Cu2+ Ions
JI He-Ming, XU Ming-Guang, ZHANG Hai-Yan, LI Xiao-Long* and QIAN Yan-Nan*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 1379-1384 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3185
October 15, 2021
TiO2:Yb3+/Tm3+, Li+, Mn2+ and Cu2+, optical characteristics
ABSTRACT
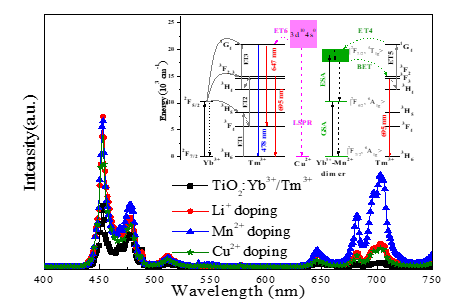
Codoping with Mn+ ions (Mn+ = Li+, Mn2+ and Cu2+)
enhanced the blue and red upconversion (UC) emissions in TiO2:Yb3+/Tm3+ nanocrystals under 980 nm excitation.
The different effects of Li+, Mn2+ and Cu2+ ions on the phase structures, morphologies and optical
characteristics of TiO2:Yb3+/Tm3+ were
discussed. The minor shifting in the diffraction peaks at 25.2°
was observed for TiO2:Yb3+/Tm3+/Li+,
and adding Mn2+ ions remained almost the same position of
diffraction peaks, while the introduction of Cu2+ ions resulted in
the shift of the diffraction peaks towards the larger angles. TiO2:Yb3+/Tm3+/Li+ and TiO2:Yb3+/Tm3+/Mn2+ nanosheets and the sphere-like TiO2:Yb3+/Tm3+/Cu2+ were observed. The mechanisms for increased UC emissions caused by adding Li+,
Mn2+ and Cu2+ ions were attributed to the tailored local
environment around Tm3+ ions, efficient energy transition between Mn2+-Yb3+ dimer and Tm3+ ions, and the localized surface plasmon resonance
(LSPR) of Cu2+ ions, respectively.