Studies on the Molecular Mechanism between HDAC8 and Inhibitory in Different Bioactivities by Molecular Docking and MD Simulations
LIANG Zhen, YAN Wen-Li, LI Hong-Mei, LI Ying and ZHANG Rong*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 1298-1308 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3126
October 15, 2021
HDAC8 inhibitors, molecular docking, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, inhibition mechanism
ABSTRACT
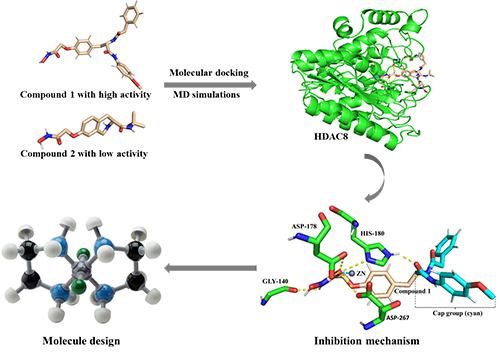
HDAC8
is an important target for the treatment of many cancers and other diseases. To
develop potent and selective HDAC8 inhibitors, molecular docking and molecular
dynamics (MD) simulations were employed for investigation of the mechanism of
HDAC8 inhibitions containing hydroxamic acid group. Compound 1 with high activity and compound 2 with
low activity were selected for comparative study. Compound 1 formed a stronger chelation with Zn ion
and was more stable in the HDAC8 pocket than compound 2. Residues HIS-180, ASP-178, ASP-267, and GLY-140 played a
critical role in securing the position of compound 1. Both the head and tail of compound 1 formed strong hydrogen bonds with ASP-178, facilitating the ZBG of
compound 1 close to the Zn ion so
that they formed permanent chelation during the simulation period. The Cap
group of the compounds with branch and long chains was advantageous to form
interaction with active pocket opening. What's more, based on the results of
this study, three innovative recommendations for the design of highly active
HDAC8 inhibitors were presented, which will be useful for the development of
new HDAC8 inhibitors.