Homochiral Coordination Polymers from Single Helices to Multiple Helices Controlled by Metal Ions
XU Zhong-Xuan*, HU Bang-Ping, LI Li-Feng and XU Shi-Fei
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 1131-1137 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3139
September 15, 2021
homochiral coordination polymers, helical chain, metal ion effect, supramolecular framework
ABSTRACT
Helix as essential molecular chiral phenomenon
at supramolecular level offers an affective me-
thod to study chiral characteristic of homochiral coordination polymers
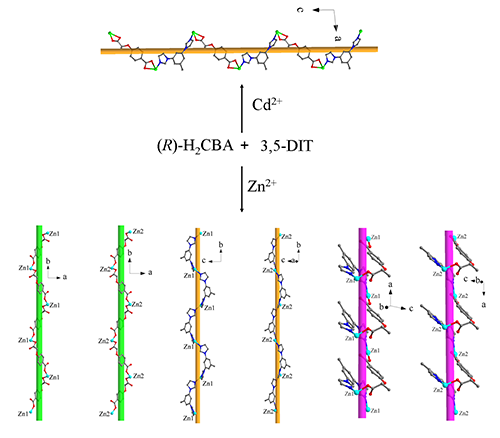
(CPs). Herein, two homochiral CPs [Cd((R)-CBA)2(3,5-DIT)]n ((R)-H2CBA = (R)-4-(1-carboxyethoxy)
benzoic acid, 3,5-DIT = 3,5-di(1H-imidazol-
1-yl)toluene, 1-R) and [Zn((R)-CBA)(3,5-DIT)]n (2-R) were synthesized under
hydrothermal conditions. In
complex 1-R, only a helical chain
was built by chiral ligands (R)-CBA2-,
ancillary ligands 3,5-DIT and Cd(Ⅱ) ions. After Cd(Ⅱ)
ions were replaced by Zn(Ⅱ) ions
under similar reaction system, Zn(Ⅱ), (R)-CBA2- and/or 3,5-DIT formed six types of helices, resulting in complex 2-R. So, the
metal ions played a key role in the construction of helical
structures. Complexes 1-R and 2-R were also characterized by elemental analysis, PXRD, TGA, CD
and UV-visible absorptions. In
addition, complexes 1-R and 2-R exhibited different
photoluminescence behaviors in solid sate compared to free ligand (R)-H2CBA.