Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Fungicidal Activity of 3-Chloro-4-(3,4-dichloroisothiazol-5-yl)- 5-hydroxy-7-methyl-2H-chromen-2-ones
LV You, LI Kun, HAO Ze-Sheng, KALININA Tatiana A., GLUKHAREVA Tatiana V.* and FAN Zhi-Jin*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 1068-1074 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3108
August 15, 2021
coumarin, synthesis, crystal structure, fungicidal activity
ABSTRACT
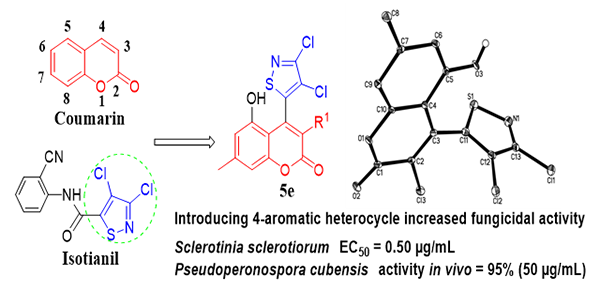
3-Chloro-4-(3,4-dichloroisothiazol-5-yl)-5-hydroxy-7-methyl-2H-chromen-2-ones, a kind of coumarin
derivatives, were synthesized by β-ketoester
formation and cyclization. Target compound 5e was crystallized from methanol
for structural identification as monoclinic crystal system, space group C2/c with a = 16.2700(6), b = 7.1801(5), c = 23.4861(10) Å, V = 2742.6(2) Å3, Z = 8, Dc =
1.756 g/cm3, F(000) = 1456
and μ = 0.827 mm-1. 8308 Reflections
were collected (6.01≤2θ≤50.05°), of which 2428
were unique (Rint =
0.0432) and used in all calculations. The final R = 0.0408 (I > 2σ(I))
and wR = 0.1056 (reflections). In vitro bioassay indicated that compounds 5d & 5e possessed good
activity against Botrytis cinerea, Physalospora piricola, Rhizoctonia solani, and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum with lower EC50 values falling between 0.50 and 4.85 µg/mL
than that of positive control osthole with its EC50 values between 7.38
and 74.59 µg/mL. In vivo screening showed that 5e exhibited 98% and 95% efficacy against Pseudoperonospora cubensis (Berk. & Curt.) Rostov. at 100 and 50 µg/mL, respectively. Our studies discovered
that the combination of bioactive substructures of isothiazole
with coumarin was an effective way to novel fungicide
development.