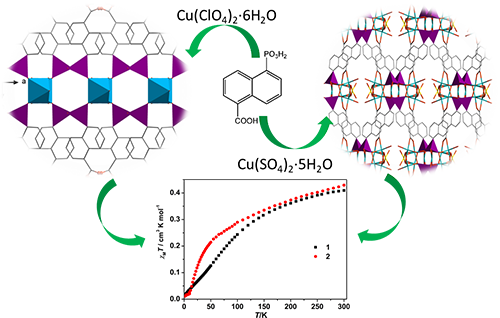
Copper Carboxylate-phosphonates: Syntheses, Crystal Structures and Magnetic Properties
XU Yan*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 1061-1067 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3085
August 15, 2021
copper, carboxylate-phosphonate, crystal structure, magnetic properties
ABSTRACT
Two
novel copper carboxyly-phosphonates, namely, Cu2.5(5-pnc)(SO4)0.5(OH)(H2O)0.5 (1) and Cu0.5(5-pncH2)(H2O)1.5 (2) (5-pncH3 = 5-phosphono-1-naphthalenecarboxylic acid), have been synthesized
and characterized by X-ray diffraction, infrared spectroscopy, elemental
analysis, and thermogravimetric analysis. In compound 1, each {PO3C} tetrahedron is corner-shared with two {Cu(1)O4},
two {Cu(2)O5} and one {Cu(3)O5}, thus forming a
one-dimensional inorganic chain along the c axis containing 8-membered rings of [Cu3O4S] and 19-membered
cages of [Cu5O10P4]. The inorganic chains are
further connected by a 5-pnc3- ligand to generate a three-dimensional
framework. Compound 2 exhibits a one-dimensional
structure, in which the inorganic chains of [Cu-O-Cu]n are connected
by the organic ligands through hydrogen
bonding interactions, forming an infinite two-dimensional layer. Magnetic measurements of 1 indicate that dominant
antiferromagnetic interactions are mediated between the Cu2+ centers.