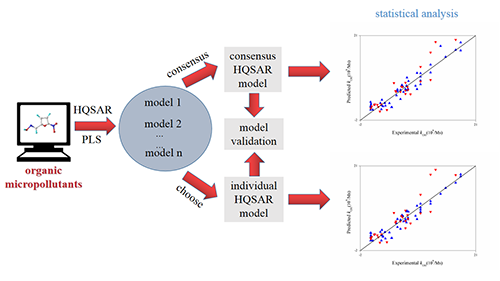
Consensus Hologram QSAR Model Studying on the Aqueous Hydroxyl Radical Oxidation Reaction Rate Constants of Organic Micropollutants
JIAO Long*, LEI Bin, QU Le, LI Rui, YAN Chun-Hua and LI Hong
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 985-993 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3083
August 15, 2021
QSPR, hologram QSAR, consensus modeling, organic micropollutants, hydroxyl radical, rate constant
ABSTRACT
The combination of hologram quantitative
structure-activity relationship (HQSAR) and consensus
modeling was employed to study the
quantitative structure-property relationship (QSPR) model for calculating the
aqueous hydroxyl radical oxidation reaction rate constants (kOH)
of organic micropollutants (OMPs). Firstly, individual HQSAR model were
established by using standard HQSAR method. The optimal individual HQSAR model
was obtained while setting the parameter of fragment distinction and fragment
size to “B” and “3~6” respectively. Secondly, consensus HQSAR model was
established by building the regression model between the kOH and the hologram
descriptors with consensus partial least-squares
(cPLS) approach. The obtained individual and consensus HQSAR model were validated
with a randomly selected external test set. The result of external test set
validation demonstrates that both individual and consensus HQSAR model are available
for predicting the kOH of OMPs. Compared
with the optimal individual HQSAR model, the established consensus HQSAR model
shows higher prediction accuracy and robustness. It is shown that the combination
of HQSAR and consensus modeling is a practicable and promising method for
studying and predicting the kOH of OMPs.