First-principles Study on the Properties of CaO(100) Surface Adsorbing Carbon Dioxide
LI Ming-Yang, LI Jia-Yu, WU Miao-Miao* and WANG Xiao-Lin
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 973-984 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3072
August 15, 2021
density functional theory, CO2 adsorption, surface chemistry, CaO(100) surface, mono-dentate ligands
ABSTRACT
The increasing carbon dioxide emissions have a huge impact on the global
environment. Carbonation reaction of CaO is regarded as a potential method to
capture carbon dioxide. The density functional theory calculations have been
performed to investigate the adsorption of CO2 on CaO(100) surface. This paper systematically
studied the adsorption of CO2 at different adsorption
sites on CaO(100) surface and the influence of adsorption angle on adsorption
energy. Based on the studying of adsorption sites, adsorption energy and
electronic structure of the CO2/CaO(100) systems, chemical
adsorption mainly happens when CO2 molecules are absorbed on
the CaO(100) surfaces, but physical adsorption may also happen. The research
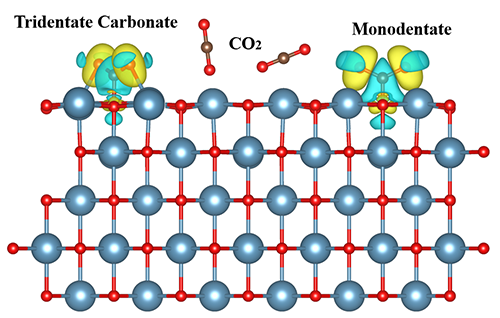
found that CO2 molecules reacted with
surface O atom through C, forming monodentate surface carbonate species and
tridentate carbonate. Among them, low-coordinated monodentate ligands have a
higher stability than tridentate ligands due to the shorter C–OS bond
length of monodentate ligands.