CoMFA Model of Anti-tumor Activity for Fluoroquinolon-3-yl s-Triazole Sulfide-ketone Derivatives and Implications for Molecular Design
FENG Hui and FENG Chang-Jun*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 703-710 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3000
June 15, 2021
fluoroquinolon-3-yl s-triazole sulfide-ketone derivative, anti-tumor activity, 3D-QSAR, comparative molecular field analysis, molecular design
ABSTRACT
Comparative
molecular field analysis (CoMFA) techniques were used to perform
three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship (3D-QSAR)
studies on the anti-tumor activity (pIH and pIC) of 28
fluoroquinolon-3-yl s-triazole sulfide-ketone derivatives (FQTSDs) against two cancer cell lines,
including human hepatoma Hep-3B cells and human pancreatic cancer Capan-1
cells. 23 compounds were randomly selected as the training set to establish the
prediction models, which were verified by the test set of 6 compounds
containing template molecule. The obtained cross-validation (Rcv2) and non-cross-validation
correlation coefficients (R2)
of the CoMFA models were 0.477 and 0.850 for pIH, and 0.421 and 0.836 for pIC, respectively. The contributions of steric and
electrostatic fields to pIH were determined to be 48.1% and 51.9%, and those to pIC were 49.4%
and 50.6%, respectively. The CoMFA models
were then used to predict the activities of the compounds in the training and
testing sets, and the models had a strong stability and good predictability.
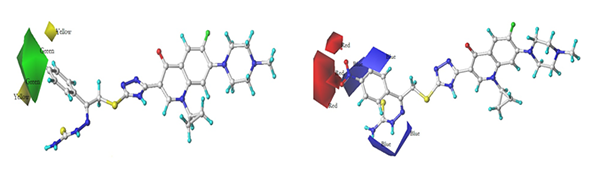
Based on the 3D contour maps, four
novel FQTSDs with a higher anti-tumor activity were designed. However, the
effectiveness of these novel FQTSDs is still needed to be verified by experimental
results.