Docking and 3D-QSAR Studies on the Imidazo[1,5-c]pyrimidine Derivative as EED Inhibitors
CHEN Xiao-Zhong, LI Guang-Ping, SHEN Yan, HU Yong, WANG Juan, WANG Yuan-Qiang* and LIN Zhi-Hua*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 689-702 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-2994
June 15, 2021
embryonic ectoderm development, CoMFA, CoMSIA, molecular docking
ABSTRACT
Embryonic
ectoderm development (EED) has become a novel target for cancer treatment. In
this study, a series of EED inhibitors was subjected to a three-dimensional
quantitative structure-activity relationship (3D-QSAR) and molecular docking. Accordingly, this is the first of such
3D-QSAR studies in a series of EED inhibitors displaying
anti-cancer pharmacological profiles. The CoMFA (q2 = 0.792, r2 = 0.994, r2pred = 0.74) and CoMSIA (q2 = 0.873, r2 = 0.994, r2pred = 0.81) models demonstrated good robustness and predictive ability.
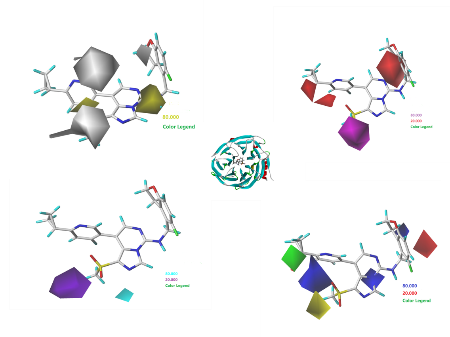
Moreover, molecular docking suggested that cation-p,p-p stacking and hydrogen bonding interactions were the
main factors affecting the activity of these inhibitors. Five new small molecules were designed based on the CoMFA and CoMSIA
contour maps. These molecules were then submitted to further ADME studies, in
which the ADME properties of the five designed molecules were found to be
within a reasonable range. In view of the corresponding findings, this study
may provide theoretical guidance for the rational design of novel EED
inhibitors.