Microstructural Exploration of the High Capacitance in RuO2-ZrO2 Coating
MA Ji-Dong*, WU Yun-Miao, JIANG Chun-Hai, ZHANG Hou-An and ZHU Jun-Qiu
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 125-135 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-2781
January 15, 2021
supercapacitor, quasi-amorphous, RuO2, ZrO2, synergistic catalysis
ABSTRACT
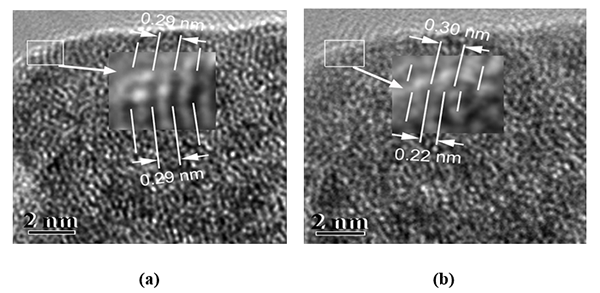
A high capacitance RuO2-ZrO2 coating was prepared
by thermal decomposition method. Extended X-ray absorption fine structure
(EXAFS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), high-resolution transmission electron
microscope (HRTEM) and ab initio calculations were applied to understand the role of the microstructure in the
acquisition of high specific capacitance of RuO2-based oxides. The results
show that the RuO2-ZrO2 oxide prepared at critical
crystallization temperature can be considered to be quasi-amorphous or
microcrystalline (A short-range ordered crystal structure can be seen from the
TEM image, but no diffraction peaks can be seen from the XRD diffraction
patterns). And this RuO2-ZrO2 was identified as a solid
solution with high solid solubility. It referred to herein as a quasi-amorphous
solid solution. Such a special microstructure was conducive for “synergistic
catalysis” owing to the cationic interaction and thus could gain high “active
site density” and high “active surface”, thus developing high specific
capacitance.