Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Fluorescence Property of a Zinc(II) Coordination Polymer with a Theoretical Calculatio
WANG Wen-Qian, CHEN Jun, WANG Shuai-Hua and WU Shao-Fan*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 79-84 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-2769
January 15, 2021
hydrothermal method, crystal structure, luminescence, theoretical calculation
ABSTRACT
We
have designed and synthesized a new luminescent coordination polymer [Zn2(NO3)(NCP)3(H2O)3]n·2nH2O
(1, HNCP = 2-(2-carboxyphenyl) imidazo-[4,5-f]-1,10-phenanthroline) under hydrothermal conditions, which has been structurally characterized by single-crystal X-ray
diffraction analyses. 1 crystallizes
in monoclinic, space group P21/n,
with a = 13.7748(3), b = 19.2651(4), c = 19.9543(4)
Å, β = 95.339(2)º, V = 5272.35(19) Å3, C60H39.73N13O13.33Zn2, Mr = 1286.80, Dc = 1.621 g/cm3, Z = 4, μ(MoKa) = 2.118, F(000) = 2629, the final R = 0.0598 and wR = 0.1483. In 1, the organic ligand NCP‒ displays two different
bridging modes to connect adjacent Zn(II) ions into a 1D chain along the c-direction. Photoluminescent
analyses reveal that 1 exhibits a
strong green emission with a fluorescent lifetime of 5.57 ns. The
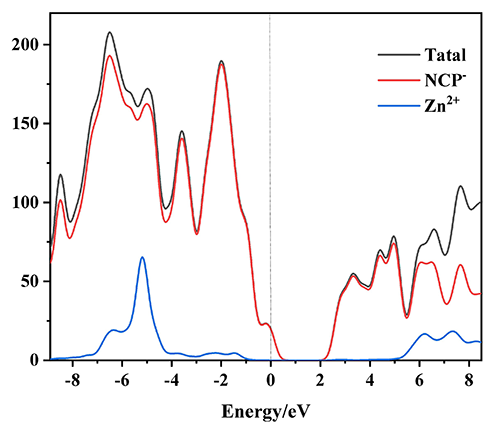
first-principle calculation results show that the luminescence mainly
originates from ligand-centered charge transition.