Water-soluble copper-based simulated enzyme: Biomimetic synthesis and activities in vitro
Yifan Kang, Xiaochen Sun, Yunluo Wang, Yanan Zhang, Wenhuan Huang*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2023, 42: 100046. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2023.100046
February 15, 2023
SOD activity, Catecholase activity, Cytotoxicity
ABSTRACT
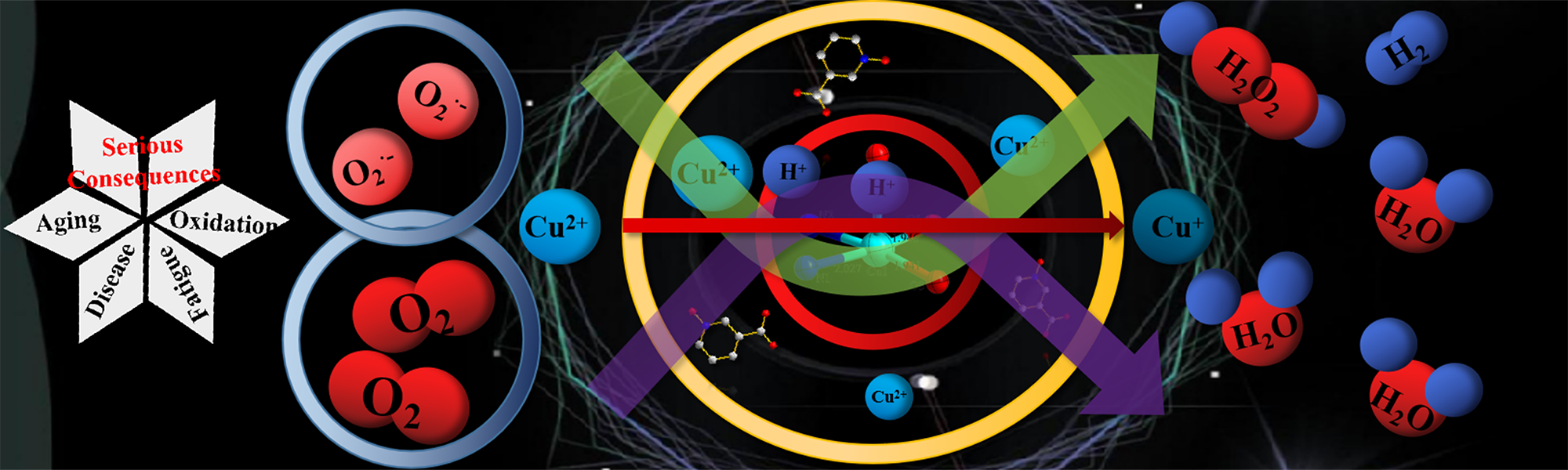
Two copper(II) complexes were obtained by solvothermal reaction induced by isonicotinic acid ligand through the study of natural simulated enzymes. The activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) 1 and 2 is higher than that of most Cu-SOD mimics, and they have the activity of catechol analogues. It is found that SOD activity and catecholase activity are directly affected by the coordination configuration of the central metal atom and the ability of the complex to accept electrons. It is also responsible for the excellent enzyme activity of these two Cu-based complexes. The results of MTT assay show that complexes 1 and 2 have no significant inhibitory effect on cell proliferation. It has good application potential in the clinical biomedical field in the future.