Cover Picture
Tandem electrocatalytic nitrate reduction reaction
Chuanfei Cang, Haoquan Zheng* Submit a Manuscript
Tandem electrocatalytic nitrate reduction reaction
Chuanfei Cang, Haoquan Zheng* Submit a Manuscript
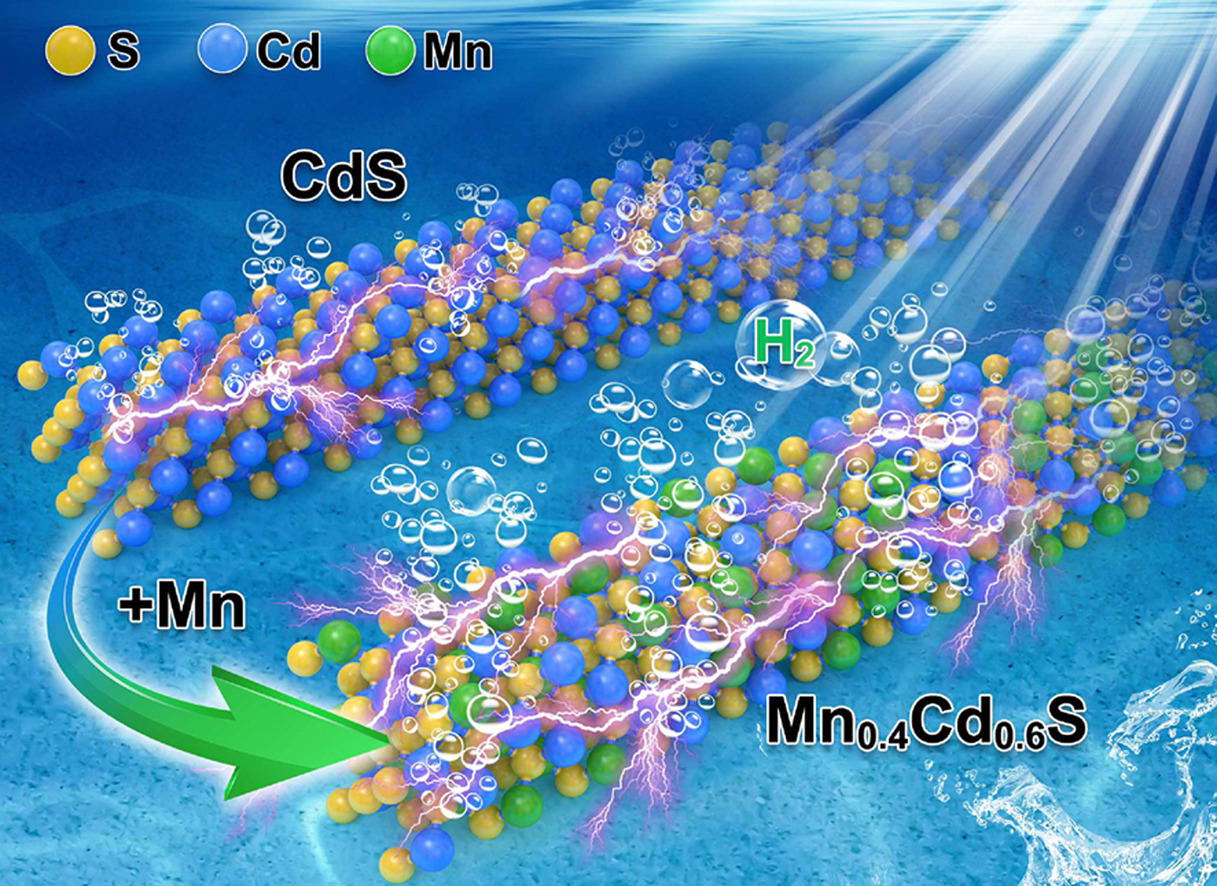
Controlled synthesis of MnxCd1−xS for enhanced visible-light driven photocatalytic hydrogen evolution
Yuxin Sun, Ye Li, Jiajia He, Liuyun Chen, Hongbing Ji, Zuzeng Qin, Tongming Su*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2023, 42: 100145. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2023.100145
MnxCd1−xS; Solid solution; Photocatalytic; Water splitting; Hydrogen
ABSTRACT
Ternary sulfide solid solutions have garnered great attention in photocatalytic water splitting due to their tunable electronic property, low cost, and sufficient light-absorption performance. Herein, a series of MnxCd1–xS samples with different Mn/Cd molar ratios were synthesized by solvothermal method and used for photocatalytic hydrogen production under visible light. The Mn0.2Cd0.8S and Mn0.4Cd0.6S are demonstrated to be the solid solutions, while Mn0.6Cd0.4S and Mn0.8Cd0.2S consist of MnxCd1–xS solid solution and MnS. In addition, the Mn0.4Cd0.6S exhibits the highest photocatalytic performance with the H2 production rate of 185.95 μmol·h−1, which is 4.7 times higher than that of CdS. Without cocatalyst, the quantum efficiency of Mn0.4Cd0.6S reaches 2.04% at 400 nm. In addition, the Mn0.4Cd0.6S solid solution also shows high stability during the photocatalytic H2 production reaction. The effect of Mn/Cd molar ratio on the microstructure, band gap structure, and photocatalytic hydrogen production performance of MnxCd1–xS was revealed systematically. The excellent photocatalytic H2 production performance of Mn0.4Cd0.6S solid solution is mainly due to its enhanced reducing potential and high charge separation efficiency.