Metal-ion-tuned metal-organic frameworks for C2H2/CO2 separation
Meng Sun, Hongyan Liu, Xiaokang Wang, Xinlei Yang, Fei Gao, Deyu Xie, Weidong Fan*, Yinfeng Han*, Ben Xu, Daofeng Sun Submit a Manuscript
Jun-Jie Fang, Zheng Liu, Yun-Peng Xie*, Xing Lu*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2023, 42: 100155. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2023.100155
September 15, 2023
ABSTRACT
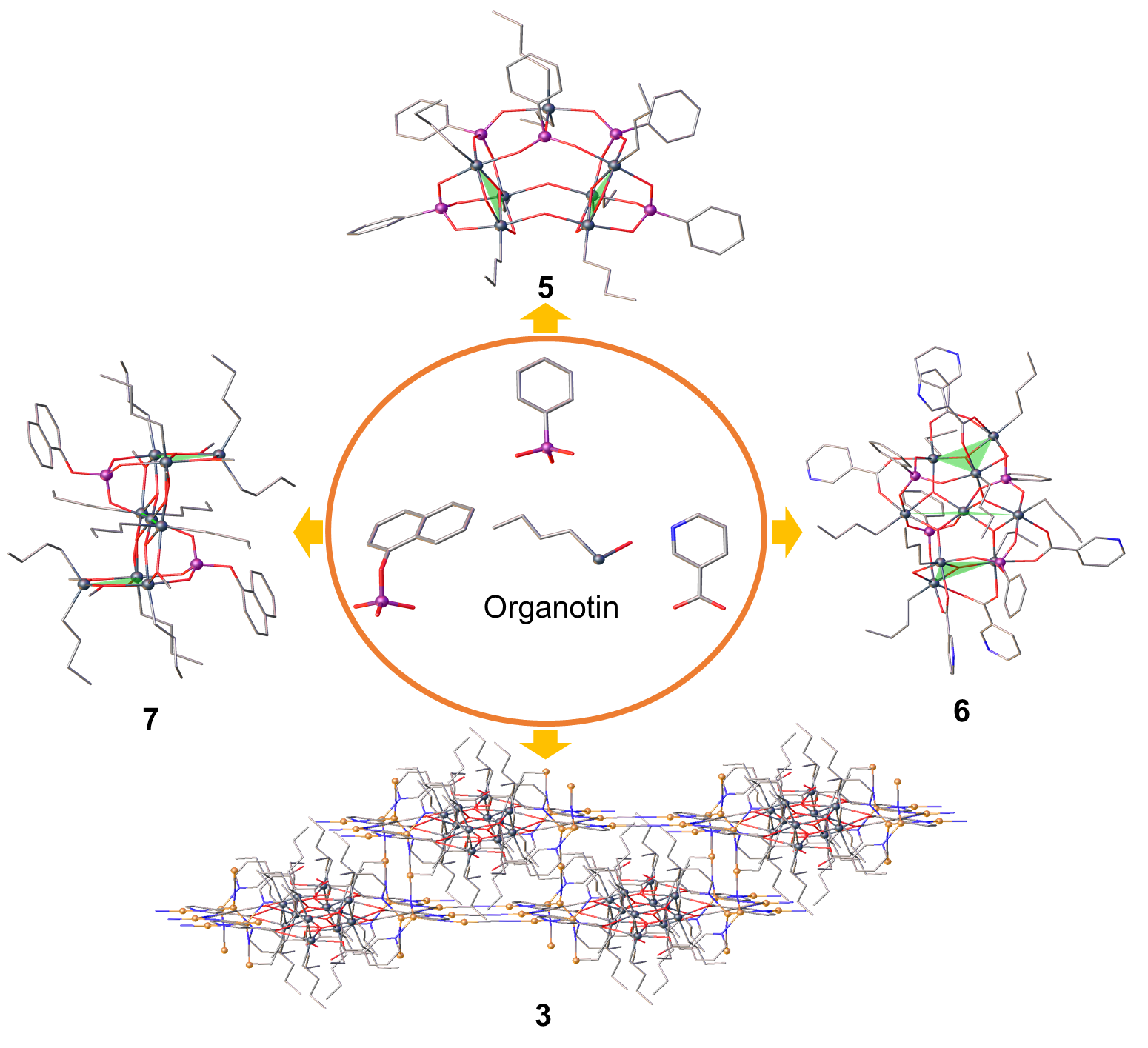
In conclusion, we have successfully synthesized a series of tin-oxo complexes using solvothermal strategies, yielding structurally diverse compounds. The crystal structures of these complexes were modulated through the incorporation of carboxylate and phosphonate ligands. Notably, we achieved the assembly of a three-dimensional cluster-based metal organic framework utilizing {Sn4} cluster units and niacin ligands with both N and O coordination sites. This framework exhibited a unique architecture with two Cu–C≡N– bridging motifs. Furthermore, we explored the influence of various precursors (such as (nBu)2SnO and nBuSn(O)OH), steric hindrances of phosphonate ligands, and solvent environments on the assembly process, resulting in the preparation of cage-dimers and ladders with distinct structural types. Analysis of the coordination patterns revealed that the carboxylate ligands adopt a staple-like coordination pattern, while the phosphonate ligands exhibit a tripod-like coordination pattern. Density of states analysis indicated that the carboxylate and phosphonate ligands contribute significantly to the electronic structure of these complexes. Overall, our findings demonstrate solvothermal synthetic strategies for the versatile self-assembly of tin-oxo complexes, providing a valuable platform for further exploration and application in this field.