Mengwen Wang, Qintao Sun, Yue Liu*, Zhengan Yan, Qiyu Xu, Yuchen Wu, Tao Cheng*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2024, 43: 100203. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2023.100203
February 15, 2024
Lithium metal batteries, Dendrite suppression, Solid electrolyte interphase, Hybrid ab initio, Reactive force field molecular dynamics, Electrolyte additives
ABSTRACT
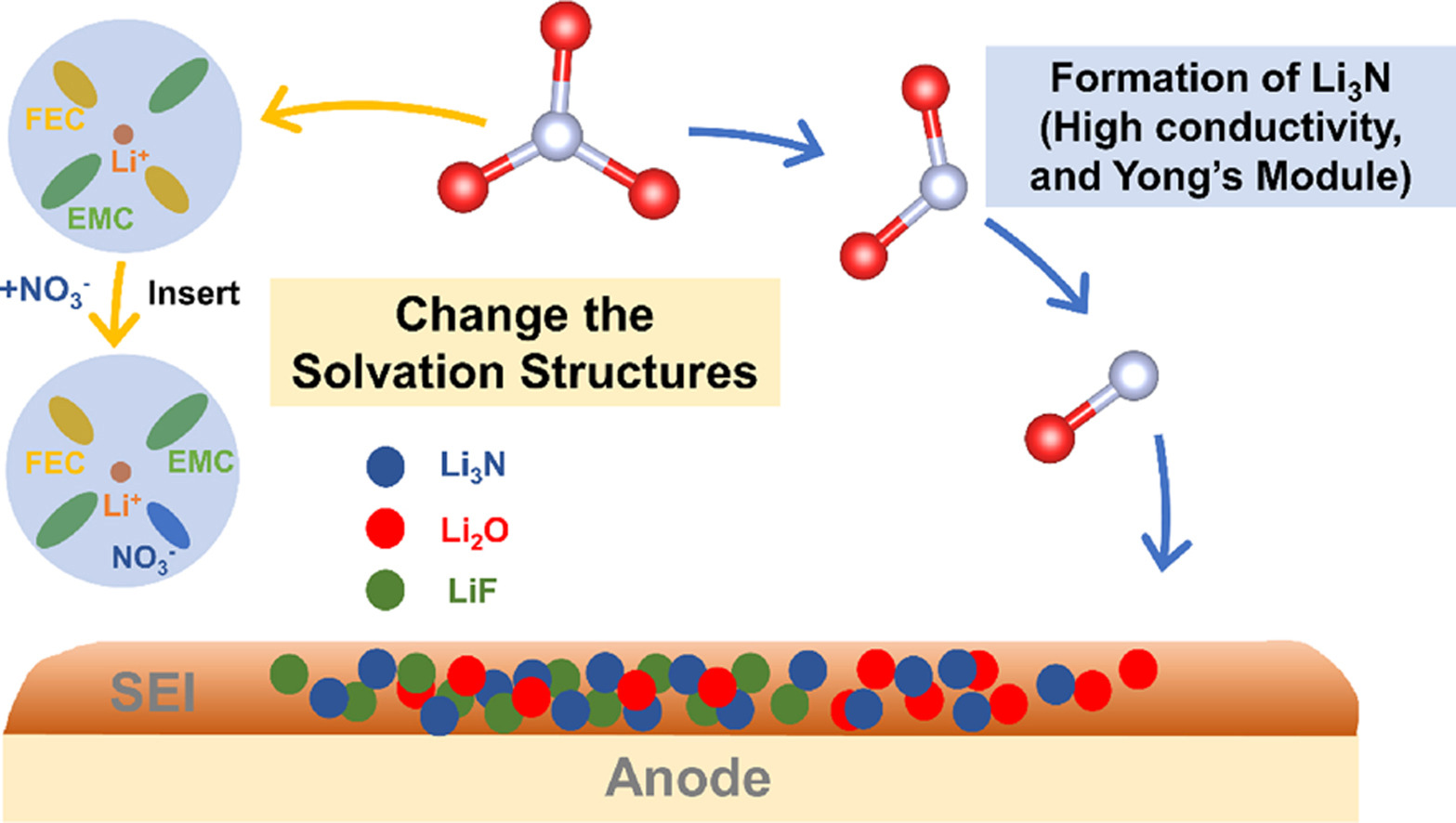
Lithium metal batteries (LMBs) represent a promising frontier in energy storage technology, offering high energy density but facing significant challenges. In this work, we address the critical challenge of lithium dendrite formation in LMBs, a key barrier to their efficiency and safety. Focusing on the potential of electrolyte additives, specifically lithium nitrate, to inhibit dendritic growth, we employ advanced multi-scale simulation techniques to explore the formation and properties of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) on the anode surface. Our study introduces a novel hybrid simulation methodology, HAIR (Hybrid ab initio and Reactive force field Molecular Dynamics), which combines ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) and reactive force field molecular dynamics (RMD). This approach allows for a more precise and reliable examination of the interaction mechanisms of nitrate additives within LMBs. Our findings demonstrate that lithium nitrate contributes to the formation of a stable and fast ionic conductor interface, effectively suppressing dendrite growth. These insights not only advance our understanding of dendrite formation and mitigation strategies in lithium metal batteries, but also highlight the efficacy of HAIR as a pioneering tool for simulating complex chemical interactions in battery materials, offering significant implications for the broader field of energy storage technology.