Insight into stable, concentrated radicals from sulfur-functionalized alkyne-rich crystalline frameworks and application in solar-to-vapor conversion
Jian-Rong Li, Jieying Hu , Lai-Hon Chung, Jilong Zhou, Parijat Borah, Zhiqing Lin, Yuan-Hui Zhong, Hua-Qun Zhou, Xianghua Yang, Zhengtao Xu*, Jun He*
Submit a Manuscript
Di Wang, Qing-Song Chen*, Yi-Ran Lin, Yun-Xin Hou, Wei Han, Juan Yang, Xin Li, Zhen-Hai Wen*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2024, 43: 100346. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2024.100346
August 15, 2024
CO2 electroreduction reaction; Bismuth-based catalysts; CO2RR devices; MEA-cell electrolyzers; Electronic structure modulation
ABSTRACT
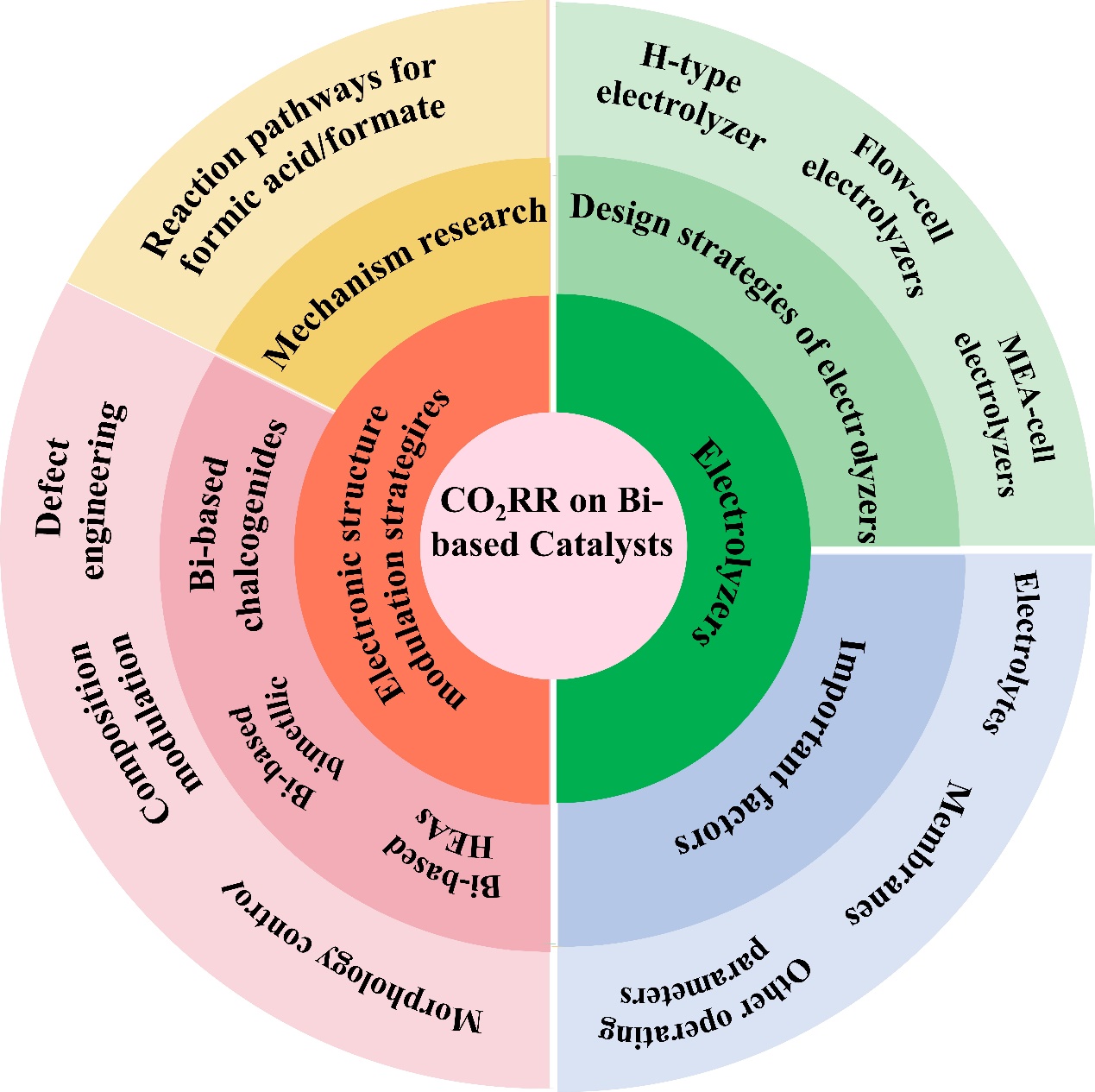
The escalating emissions of greenhouse gases into atmosphere have precipitated a host of ecology and environmental concerns. Electrochemical reduction of CO2 (CO2RR) is emerging as a sustainable solution for effectively addressing these issues. Leveraging the cost-effectiveness and eco-friendly attributes, Bi-based catalysts have been extensively studied with the purpose of enhancing activity and stability. This minireview majorly overviews the research advancements in Bi-based catalysts for CO2 electrocatalysis towards formic acid/formate production. Initially, we offer a concise overview of the reaction pathways involved in electrochemical CO2 reduction. Subsequently, we summarize the progress in various types of electrolysis cells and associated influencing factors. Specifically, the electronic structure modulation strategies of Bi-based catalysts including oxide-derived bismuth, bismuth-based chalcogenides, bimetallic and high-entropy compounds, etc. have been highlighted. Future research endeavors are poised to delve deeper into comprehending system dynamics during the reaction process to achieve exemplary stability high energy efficiency under industrial conditions.