Nitrogen doping retrofits the coordination environment of copper single-atom catalysts for deep CO2 reduction
Yuxiang Zhang, Jia Zhao, Sen Lin*
Submit a Manuscript
Liang Ma, Zhou Li, Zhiqiang Jiang, Xiaofeng Wu*, Shixin Chang, Sónia A.C. Carabineiro*, Kangle Lv*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2024, 43: 100416. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2024.100416
November 15, 2024
Graphitic carbon nitride; Photocatalytic NO oxidation; Photocatalytic CO2 reduction; Urea
ABSTRACT
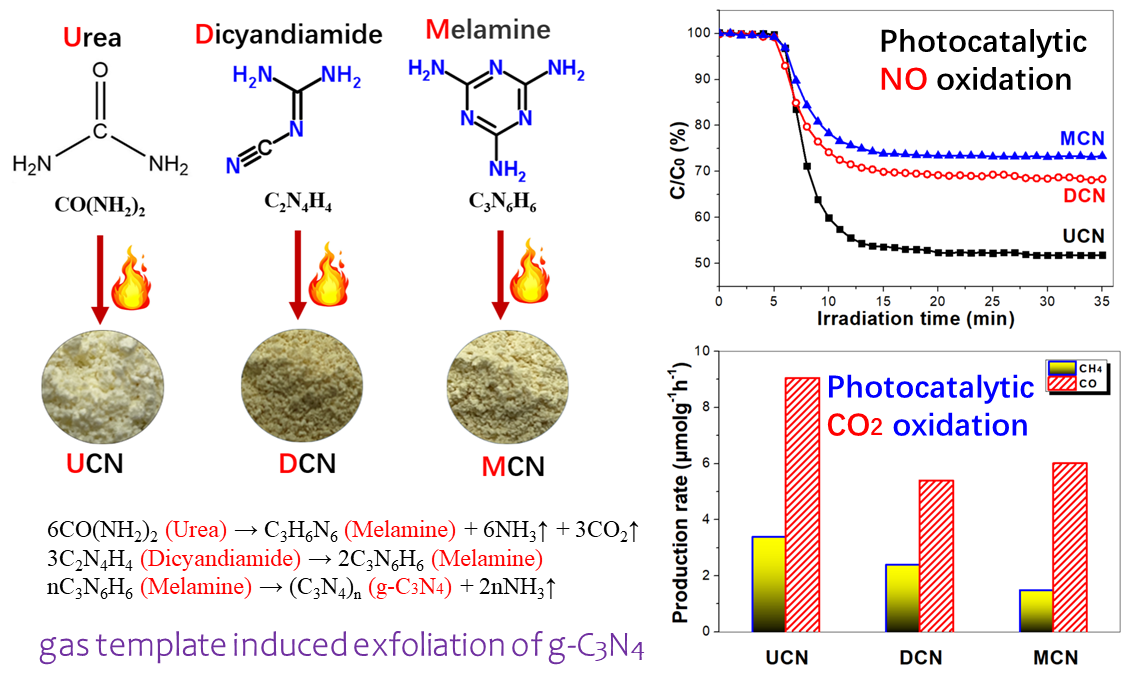
Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4, CN) is recognized as the most extensively studied organic polymeric photocatalyst for pollution control and energy conversion due to its facile synthesis and suitable electronic band structure. The aim of the present work is to explore the effect of precursors, such as urea (U, (NH2)2CO), dicyandiamide (D, C2H4N4) and melamine (M, C3H6N6), on the structure and photocatalytic activity of the obtained CN samples, denoted as UCN, DCN and MCN, respectively. The sheet-like UCN sample shows significantly enhanced photoreactivity in both NO oxidation and CO2 reduction compared to the bulk DCN and MCN materials. In addition, UCN demonstrates the ability to suppress the formation of toxic NO2 intermediate during the photocatalytic oxidation of NO. The improved photocatalytic activity of UCN can be attributed to a dual effect: first, its increased specific surface area provides more active sites for the photocatalytic reaction; second, it exhibits a stronger affinity for substrates like NO and CO2, which facilitates charge migration at the interface.