Alkyl-linked TiO2@COF heterostructure facilitating photocatalytic CO2 reduction by targeted electron transport
Jiangqi Ning, Junhan Huang, Yuhang Liu, Yanlei Chen, Qing Niu, Qingqing Lin, Yajun He, Zheyuan Liu, Yan Yu, Liuyi Li* Submit a Manuscript
Guanyang Zeng, Xingqiang Liu, Liangqiao Wu, Zijie Meng, Debin Zeng*, Changlin Yu*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2024, 43: 100462. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2024.100462
December 15, 2024
Bi2O2CO3 nano-sheet; I- doping; Ion exchange; Band gap energy; Photocatalytic performance
ABSTRACT
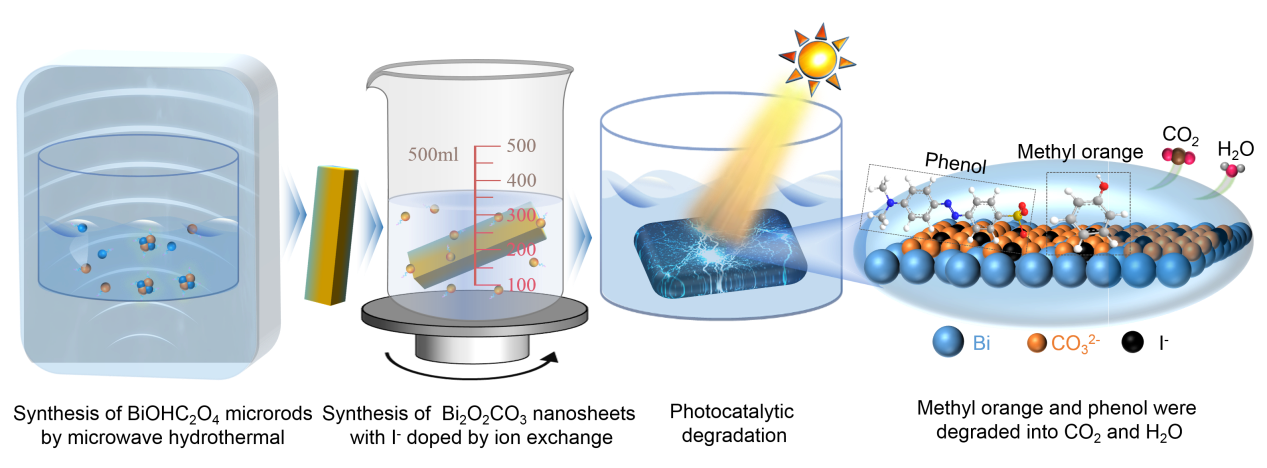
Here, we report a novel visible-light-driven I− doped Bi2O2CO3 nano-sheet photocatalyst synthesized via a facile ion exchange route at room temperature. This obtained Bi2O2CO3 nano-sheet with I− doping shows several advantages. The specific surface area of I0.875-Bi2O2CO3 is 2.16 times higher than that of Bi2O2CO3, providing more catalytic sites for the degradation reactions. Moreover, a 3.2 times photocurrent enhancement is observed in I0.875-Bi2O2CO3 compared with Bi2O2CO3, producing more photogenerated electron-hole pairs for degradation. The synergistic effect between texture property and photoelectric effect boosts the removal of organic pollutants. Under visible light illumination, I0.875-Bi2O2CO3 displays superior photocatalytic performance for the degradation of methyl orange (MO) and phenol. Notably, a phenol degradation rate, 88%, is achieved by I0.875-Bi2O2CO3 with illuminating for 60 min, which is about 29 times higher than that of pristine Bi2O2CO3. This finding may provide an opportunity to develop a promising I− doped catalyst for organic pollutants removal.