Alkyl-linked TiO2@COF heterostructure facilitating photocatalytic CO2 reduction by targeted electron transport
Jiangqi Ning, Junhan Huang, Yuhang Liu, Yanlei Chen, Qing Niu, Qingqing Lin, Yajun He, Zheyuan Liu, Yan Yu, Liuyi Li* Submit a Manuscript
Guixu Pan, Zhiling Xia, Ning Wang*, Hejia Sun, Zhaoqi Guo*, Yunfeng Li*, Xin Li
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2024, 43: 100463. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2024.100463
December 15, 2024
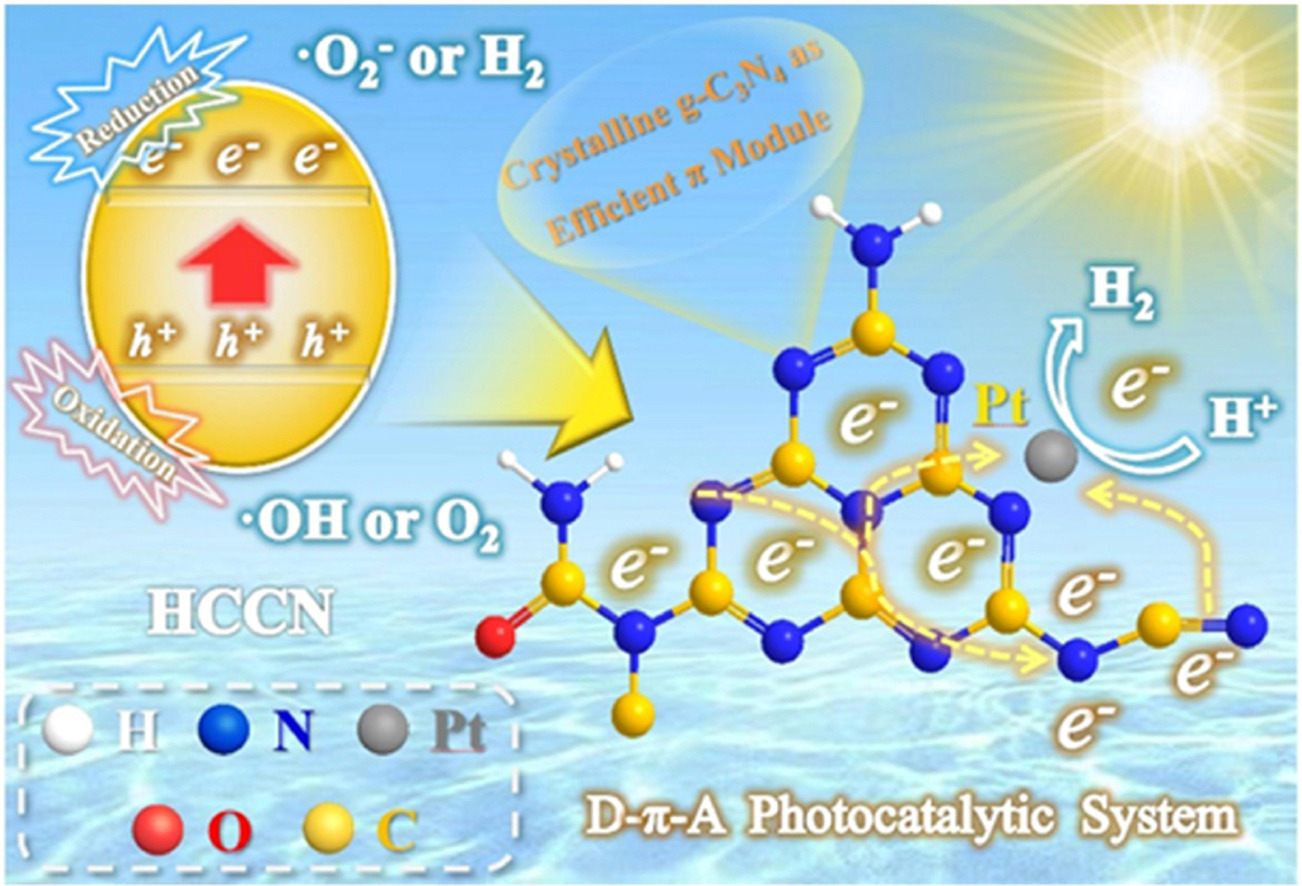
Photocatalysis; g-C3N4; D-π-A structure; Crystallinity regulation; H2 production
ABSTRACT
Donor-π-acceptor (D-π-A) type photocatalysts with g-C3N4 as π-module have attracted much attention due to their optimized conjugate structure and enhanced electron directed driving. However, the inefficient charge migration of g-C3N4 due to its amorphous or semi-crystalline structure and limitation of available functional groups are present challenges. In this work, the D-π-A type high crystalline carbon nitride (HCCN) has been obtained by in-situ introducing amide and cyanide groups into the high-crystallinity melon framework. The synergistic effect of functional group modification and crystallinity regulation greatly enhances the electron induction driving and charge carrier density. Moreover, the density functional theory (DFT) calculations demonstrate that the D-π-A structure could induce the local charge distribution of melon units to provide a unique and stable pathway for photoinduced charge migration. The as-prepared HCCN sample shows a superior visible-light photocatalytic performance for hydrogen evolution with an apparent quantum efficiency (AQE) of 12.2% at 420 ± 15 nm, which is 23.7 times higher than that of original g-C3N4. Finally, the charge separation and transfer processes as well as the possible photocatalytic reaction mechanisms of HCCN sample are also investigated.