Alkyl-linked TiO2@COF heterostructure facilitating photocatalytic CO2 reduction by targeted electron transport
Jiangqi Ning, Junhan Huang, Yuhang Liu, Yanlei Chen, Qing Niu, Qingqing Lin, Yajun He, Zheyuan Liu, Yan Yu, Liuyi Li* Submit a Manuscript
Linping Li, Junhui Su, Yanping Qiu, Yangqin Gao, Ning Li*, Lei Ge*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2024, 43: 100472. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2024.100472
December 15, 2024
Microsphere; S-scheme heterojunction; Schottky junction; Synergistic effect; Photocatalytic hydrogen evolution
ABSTRACT
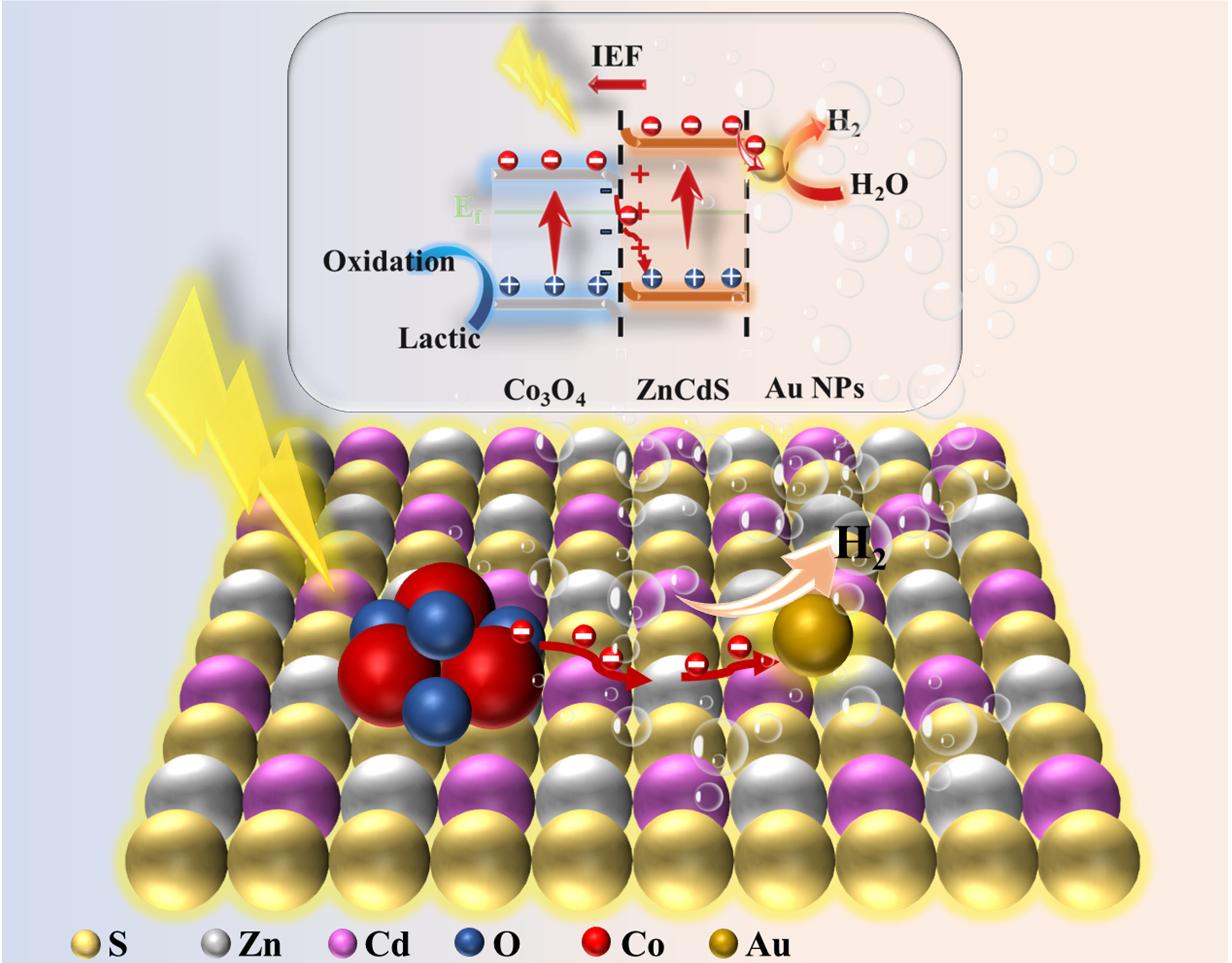
Promoting efficient carrier separation and transfer can largely enhance photocatalytic performance and inhibit photo-corrosion. In this work, ZnCdS (ZCS) microspheres were obtained by a self-assembly strategy, and the Au/Co3O4/ZCS composites were synthesized by a modified photo-deposition method (loading Co3O4 and Au onto the surface of ZnCdS). The synergistic effect between the S-scheme heterojunction (Co3O4/ZCS) and Schottky junction (Au/ZCS) can effectively promote the generation and separation of photoelectrons and holes, thus enhancing the photocatalytic activity. Under visible light, the efficient photocatalysts showed hydrogen production activities up to 2525 μmol g−1 h−1, which is 2.24 times higher than that of Co3O4/ZCS and 6.92 times higher than that of pure ZnCdS. DFT calculations indicate that the built-in electric field between Co3O4/ZCS provides the driving force for efficient electron-hole separation, and the Au nanoparticles (NPs) act as electron collectors at the interface of ZnCdS to capture the electrons, which effectively prolongs the lifetime of photoelectrons and further enhances the photocatalytic hydrogen production activity.