Cover Picture
Ni(OH)2 Derived from NiS2 Induced by Reflux Playing Three Roles for Hydrogen/oxygen Evolution Reaction
Sheng-Jun Xu*, Ya-Nan Zhou, Guo-Ping Shen and Bin Dong* Submit a Manuscript
Ni(OH)2 Derived from NiS2 Induced by Reflux Playing Three Roles for Hydrogen/oxygen Evolution Reaction
Sheng-Jun Xu*, Ya-Nan Zhou, Guo-Ping Shen and Bin Dong* Submit a Manuscript
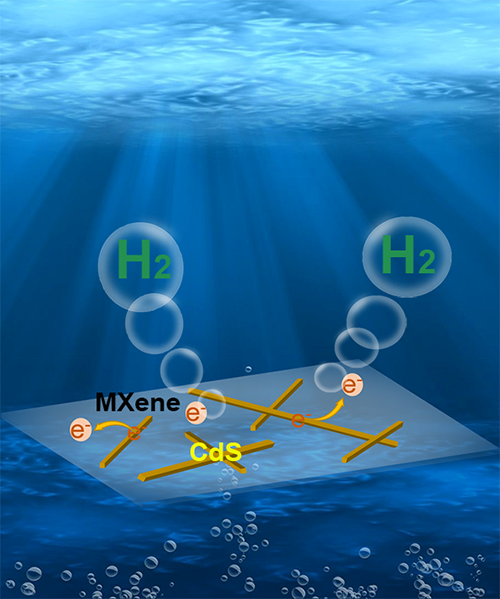
Synergism of 1D CdS/2D Modified Ti3C2Tx MXene Heterojunctions for Boosted Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production
Shi Cheng, Qianqian Xiong, Chengxiao Zhao* and Xiaofei Yang*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2208058-2208064 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2022-0151
July 25, 2022
CdS, MXene, heterojunction, water splitting, hydrogen evolution reaction
ABSTRACT
Rational design and controllable synthesis of
visible-light-responsive photocatalysts that exhibit both good
hydrogen-producing efficiency and stability in the water splitting reaction are
undoubtedly a challenge. Here we report an integrated CdS
nanorod/oxygen-terminated Ti3C2Tx MXene
nanosheet heterojunction with a high catalytic hydrogen evolution reaction
(HER) activity. By incorporating one-dimensional (1D) CdS nanorods onto
annealed ultrathin two-dimensional (2D) MXene nanoshees, the mixed-dimensional
1D/2D heterojunction achieved a hydrogen-evolving rate of 8.87 mmol × g-1 × h-1, much higher than that of bulk CdS and
CdS/unmodified MXene hybrid catalysts. The enhanced HER activity and stability
of the designed heterojunction catalyst are attributed to the presence of
oxygen-containing terminal groups on the surface of thermally treated Ti3C2Tx MXene, extended light absorption spectra as well as the precisely-constructed
intimate Schottky contact, implying an accelerated interfacial charge transfer
and efficient, long-term photocatalytic hydrogen production performance. The
results demonstrate that oxygen-terminated 2D MXene can be well utilized as a
functional platform for the development of novel heterojunctioned
photocatalysts.