Hierarchical Pt/NiO hollow nanofibers for catalytic oxidation of HCHO at room temperature
Xinyu Zeng, Zhuofan Zeng, Qingqing Hu, Kejun Liu, Lei Ming, Bei Cheng, Wang Wang*, Guoqiang Luo, Shaowen Cao* Submit a Manuscript
Qijun Tang, Wenguang Tu*, Zhigang Zou
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2025, 44(6), 100597. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2025.100597
June 1, 2025
ABSTRACT
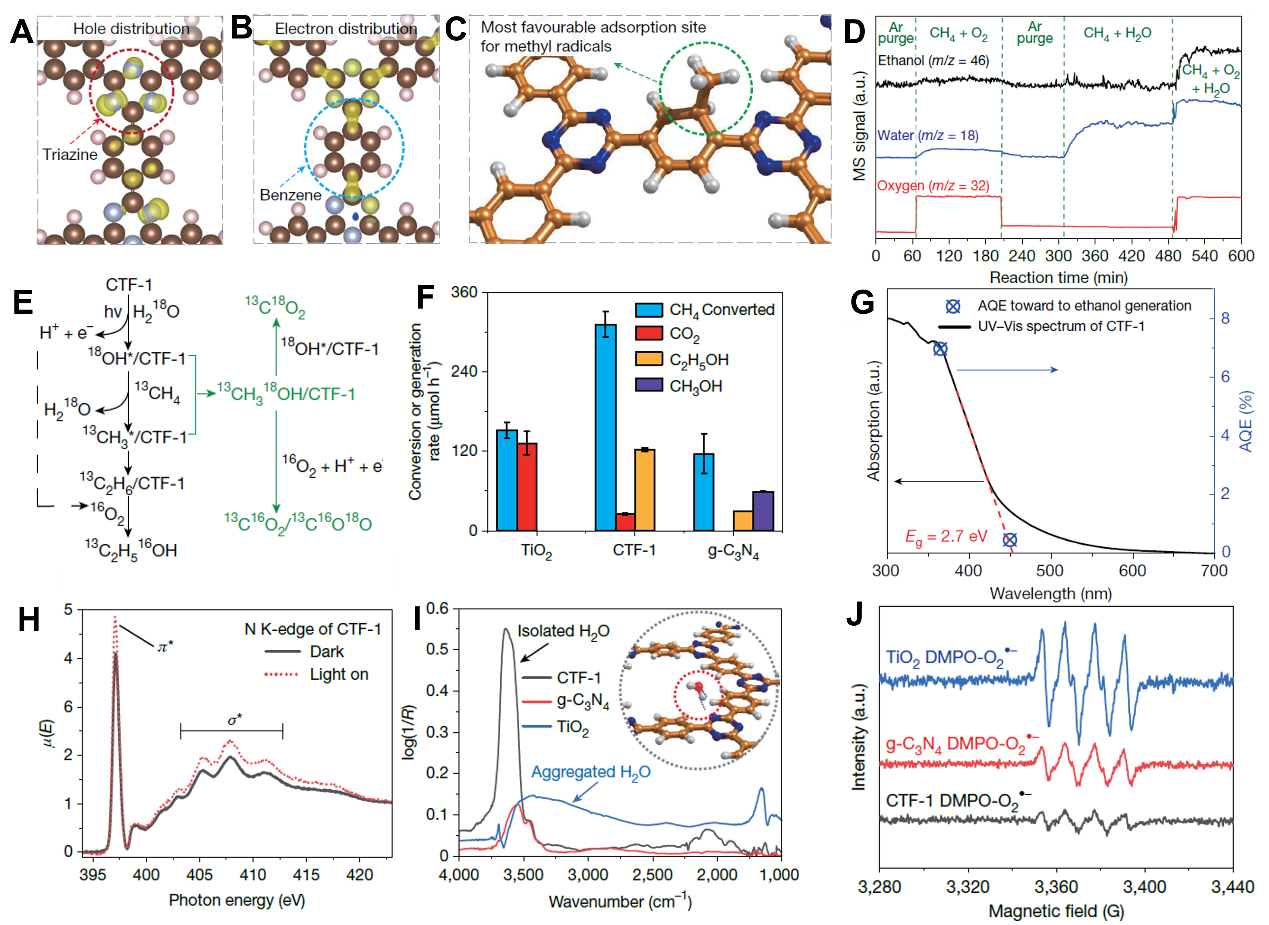
In summary, they demonstrated the intrinsic
“intramolecular heterojunction” in CTF-1 polymer is highly selective for
solar-driven methane to ethanol reaction. Such activity and selectivity can be
ascribed to the intrinsic and simultaneous charge separation by the
“intramolecular heterojunction”, stronger water adsorption, highly selective
water-promoted C–H bond cleavage, favorable reaction sites on the benzene motif
and the preferred desorption of ethanol to methanol. This work provides a novel
approach for converting methane into high-value products under mild conditions.
Additionally, the introduction of the new concept “intramolecular junction”
offers innovative solutions to critical challenges in the design of
photocatalysts.