Cover Picture
Borosilicates as deep-ultraviolet transparent nonlinear optical crystals: structural motifs, performance limits and future directions
Yangfeifei Ou, Xiao-Liang Zhou, You-Zhao Lan, Jian-Wen Cheng* Submit a Manuscript
Borosilicates as deep-ultraviolet transparent nonlinear optical crystals: structural motifs, performance limits and future directions
Yangfeifei Ou, Xiao-Liang Zhou, You-Zhao Lan, Jian-Wen Cheng* Submit a Manuscript
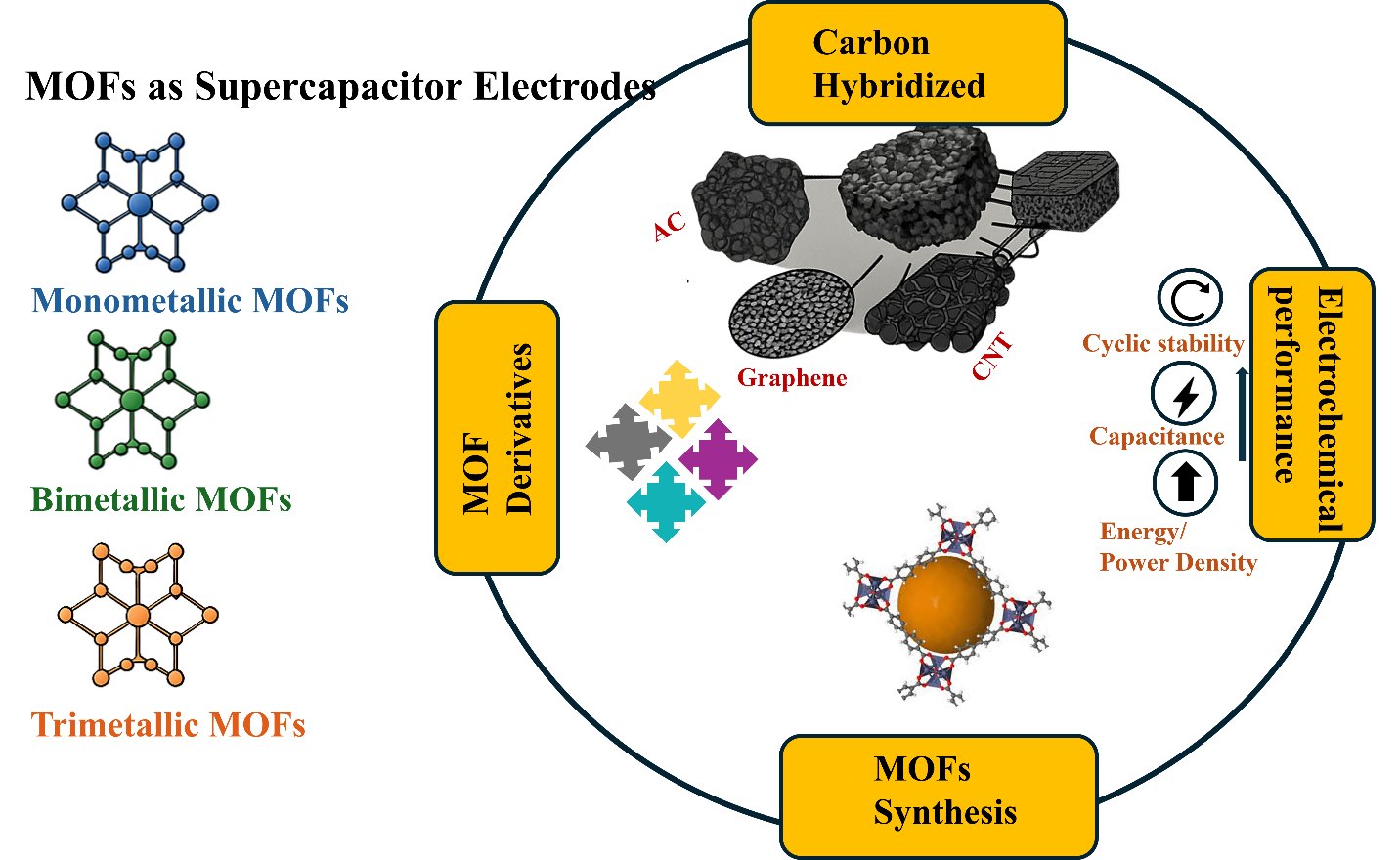
A comprehensive review: MOFs and their derivatives as high-performance supercapacitor electrodes
Malaika Arshad, Zia Ul Haq Khan*, Swera Talib, Sana Sabahat, Noor Samad Shah, Huma Ajab, Farooq Ahmad, Syed Khasim, M.A. Diab*, Heba A. El-Sabban*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2025, 44(9), 100676. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2025.100676
September 1, 2025
MOFs; Energy storage; Different metallic MOF; Supercapacitor
ABSTRACT
An expanding human population and technological progress demand clean and effective energy-storing systems. Within the realm of energy-storing devices, Supercapacitors have grabbed huge focus owing to their high-power density, unique cycling stability, and fast charging discharging capabilities. Electrode material has a prominent impact on the effectiveness of supercapacitors. Several types of electrode materials have been used, encompassing varied metal oxides, activated carbon, conducting polymers, and MOFs. Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) are considered emerging electrode candidates, which could be ascribed to the tunable porosity, large surface areas, and designed morphology. This review shows a detailed analysis of various mono, bi, and trimetallic MOFs along with derivatives in supercapacitor applications, their structural characteristics, and synthetic strategies. It also critically evaluates MOFs potential to boost the supercapacitor’s energy density, power density, stability, and conductivity. It also underscores their significance in the establishment of future-oriented energy storage applications.