Cover Picture
Chiral europium-organotin oxo-clusters with dual-emission circularly polarized luminescence
Gui-Xin Yan, Er-Xia Chen, Jin-Xia Yang, Jian Zhang*, Qipu Lin * Submit a Manuscript
Chiral europium-organotin oxo-clusters with dual-emission circularly polarized luminescence
Gui-Xin Yan, Er-Xia Chen, Jin-Xia Yang, Jian Zhang*, Qipu Lin * Submit a Manuscript
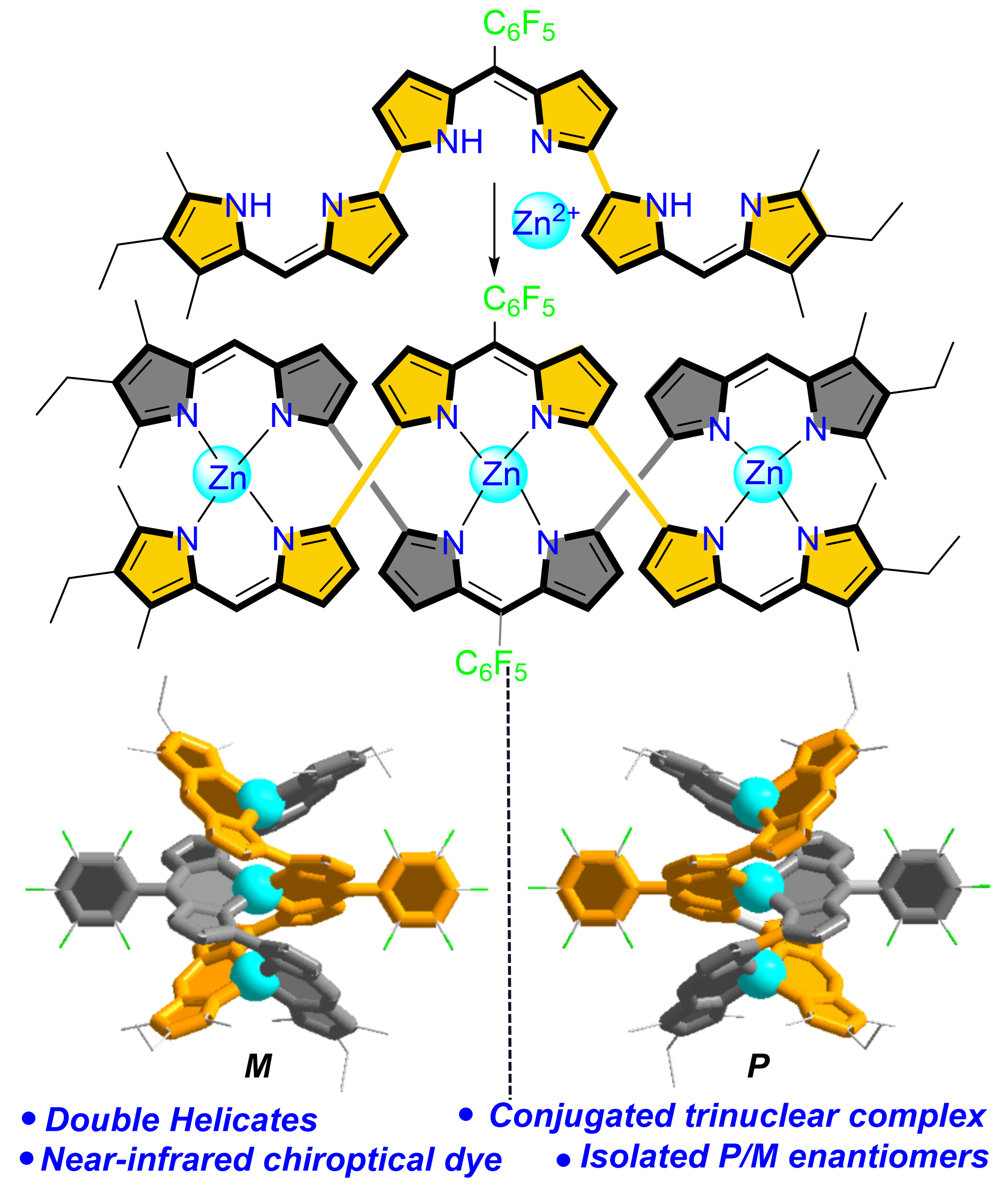
A stereochemically stable double-helical trinuclear bis(tridipyrrin) complex exhibiting near-infrared chiroptical properties
Yingjian Shang, Xuefeng Zhao, Tao Wu, Yanhui He, Xing Guo, Hongwei Si*, Lijuan Jiao*, Erhong Hao*, Wei Miao*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2025, 44(12), 100722. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2025.100722
December 1, 2025
Double-helical trinuclear complex; Zinc coordination complex; Tridipyrrin ligands; Chiral near-infrared dyes; Circular dichroism
ABSTRACT
A novel double-stranded trinuclear bis(tridipyrrin) zinc(II) complex, constructed from a linear π-conjugated tridipyrrin ligand, was synthesized and characterized. The complex featuring six directly linked dipyrrin units, exhibits a stable double-helical structure with two non-superimposableP and Menantiomers, as confirmed by X-ray crystallography. Chirality was further demonstrated through HPLC separation and mirror-image circular dichroism (CD) spectra. The complex shows strong near-infrared (NIR) absorption and excellent solubility in various solvents, attributed to its sterically hindered structure. Spectroscopic, electrochemical, and theoretical studies revealed its unique electronic properties and redox behavior. This work advances the design of chiral NIR-active metallo-supramolecular systems and highlights potential applications in chiroptical materials.