Just Accepted
Just Accepted Articles have been posted online after technical editing and typesetting for immediate view. The final edited version with page numbers will appear in the Current Issue soon.
Submit a Manuscript

Modulating charge kinetics in CDs/CTF S-scheme hybrids for enhanced H₂O₂ photosynthesis
Haoyuan Qin, Lijing Wang, Yuanhao Tang, Weilong Shi*, Changyu Lu*
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjsc.2025.100858
Covalent triazine frameworks; N, S-CDs; S-scheme heterojunction; H2O2; photocatalysis
ABSTRACT
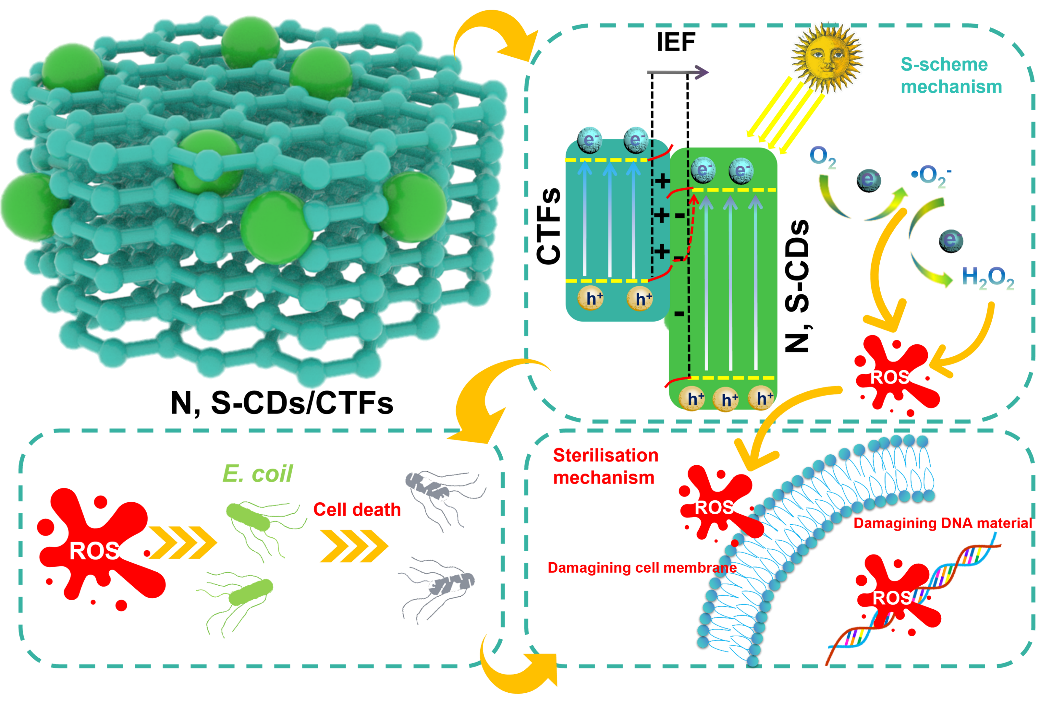
The demand for green production of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) has triggered extensive research on photocatalytic synthesis, but there are still problems of low catalytic efficiency. Herein, N, S co-doped carbon dots (N, S-CDs) were anchored on the covalent triazine frames (CTFs) to successfully form the N, S-CDs/CTFs S-scheme heterojunction by a simple hydrothermal method for achieving the optimal photocatalytic H2O2 production rate of 10350 μM g-1 h-1 in pure water. Between the interface of N, S-CDs and CTFs, a five-membered or six-membered nitrogen-containing and sulphur-containing heterocycles linked together to accelerate the electron transfer rate through the conjugation effect. In addition, the S-scheme heterostructure can effectively form an internal electric field (IEF) at the interface, which can promote the separation of electrons and holes. For practical application, the H2O2 produced by the N, S-CDs/CTFs composite photocatalytic system can also be used for photocatalytic antimicrobial treatments, which achieved a bactericidal rate of 86% against E. coli, which is 28% higher than that of pure CTFs. The design displays great potential in the fields of photocatalytic H2O2 generation and photocatalytic antimicrobial, and it also makes the photocatalytic antimicrobial technology more stable and efficient, meanwhile, it also expands a new direction for the application of homogeneous CDs in photocatalysis.