Synthesis, Structural Characterization, Fluorescence Properties and Herbicidal Activity of Bis(substituted salicylaldehyde) Carbohydrazide Dibutyltin Complexes
FENG Yong-Lan, JIANG Wu-Jiu, ZHANG Fu-Xing and KUANG Dai-Zhi*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 1639-1646 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3214
December 15, 2021
bis(substituted salicylaldehyde) carbohydrazide dibutyltin, fluorescence properties, herbicidal activity
ABSTRACT
A series of dibutyltin complexes, (Bu2Sn)2L,
[(Bu2Sn)2L]3 and H2LSnBu2,
were synthesized by microwave-assisted methanolic solvothermal
method, where H4L is [2-(OH)-R-ArCH=NNH]2CX, and X = O, R
= 4-NEt2 (T1), 5-Br (T2); X = S, R = H (T3); R = 5-Br (T4). Their structures were
characterized by elemental analysis, IR and (1H, 13C)-NMR
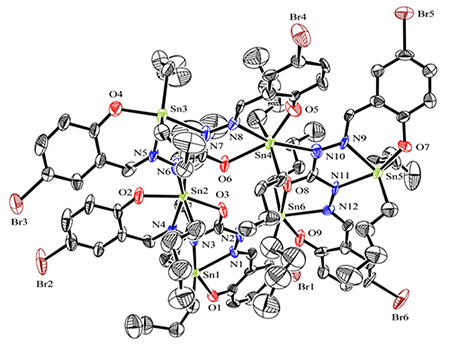
spectra. The molecular structure of T2 was confirmed by X-ray diffraction. The crystal of T2 belongs to monoclinic system, space group Ia. Five-coordinated distorted triangular bipyramids and
six-coordinated distorted octahedral configurations were formed by the
coordination of oxygen and nitrogen atoms of ligand with two dibutyltins, thus forming a trimeric
hexanuclear butyltin complex by the cross coordination of three units (Bu2Sn)2L
with enol imines. The T2 and T4 exhibit fluorescence emission in DMF
solvents and DMF-water mixture. The fluorescence intensity of T2-DMF-H2O system decreases
almost linearly with the increase of water volume fraction (WVF). The aggregation
fluorescence enhancement effect of T4-DMF-H2O
solution system increases with the increase of WVF at the range of 0~20% WVF. When
WVF is more than 20%, the fluorescence intensity decreases with the increase of
WVF. In addition, T1~T4 have broad growth activities on
target plants, such as Portulaca oleracea L., Amaranthus spinosus L., Cassia tora L., Brassica campestris L.ssp.chinensis
var.utilis Tsen et Lee, and Amaranthus
tricolor L., and can be used as a candidate herbicide for further research.