Conversion of Methane to Ethylene with BaCe0.9Y0.1CoxO3-δ Hydrogen Permeation Membrane
LIU Yun, YUAN Sheng-Ze and XIE Kui*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 901-907 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3055
July 15, 2021
mixed-conducting, dehydrogenation, methane, metal nanoparticle, membrane
ABSTRACT
Dehydrogenation
coupling of methane (DCM), which can be effectively used to produce low carbon alkenes,
has the advantages of rich raw materials, simple reaction device, low energy
consumption, etc. Herein, we report a series of Co doped perovskite
porous-dense BaCe0.9Y0.1CoxO3-δ (BCYCx) membrane for DCM. After treatment
in a reduced atmosphere, a large number of Co nanoparticles will exsolute on the surface of BCY. The metal-oxide interface
is helpful to activate the C–H bonds, inhibit the carbon deposition, and so on.
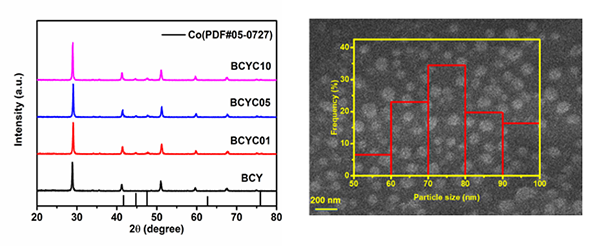
The XRD, SEM and XPS prove that Co nanoparticles homogeneously distributed on the
BCYCx porous layers, which will create a large quantity of catalytic
active sites. At 1100 ℃, the highest concentration
of C2 product was 5.66% (5.25% ethane + 0.41% ethylene) in output
gas when methane conversion reaches a maximum value of 24.8%, and the C2 selectivity gets to 45.6%. We further demonstrate the catalytic performance of
high-temperature DCM without obvious decrease after running for 30 hours.