Solvothermal Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Characterization of a New Binuclear Copper(II) Complex with K3:N1:N2:N4-3-(Pyridin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazole (HPT)
LI Chong-Yu and YU Peng*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 453-458 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3049
April 15, 2021
binuclear copper(II) complex, thermal stability, fluorescence, magnetic property
ABSTRACT
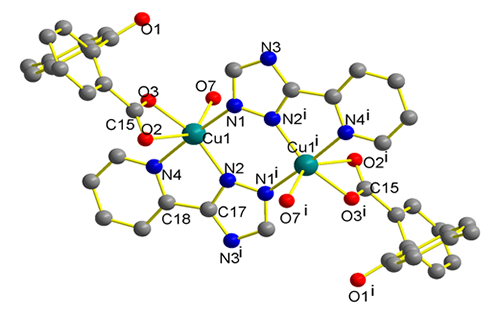
A new binuclear copper(II) complex [Cu2(MBBA)2(HPT)2(H2O)2]·2H2O (1) was synthesized with copper acetate, 2-(4-methylbenzoyl) benzoic acid (MBBA)
and 3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole (HPT). It crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/c with a = 14.722(2), b = 8.8907(12), c =
18.5565(18) Å, β = 116.820(7)º, V = 2167.6(5) Å3, Mr = 483.96, Dc = 1.483 g/cm3, Z = 4, μ(MoKa) = 1.049 mm-1, F(000) = 981, the final GOOF = 0.952, R = 0.0586 and wR = 0.0823. The whole molecule consists of two copper ions bridged by two HPT
molecules. The central Cu(II) ion is
coordinated by six atoms to give a distorted octahedral coordination
geometry. The structure of 1 has been determined by X-ray
diffraction, IR spectrum and thermal stability analysis. The solid-state
fluorescence displays an obvious emission band at 412 nm upon excitation at 330
nm. Magnetic properties indicate that 1 exhibits antiferromagnetic properties.