A Study on the Preparation of Konjac Glucomannan-Silk Fibroin Composite Aerogels and Its Adsorption of Water Pollutant Cr(Ⅲ)
CHEN Han, WU Chun-Hua*, HUANG Yi, WU Hua-Hua and PANG Jie*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 23-30 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-2774
January 15, 2021
konjac glucomannan, silk fibroin, aerogel, adsorption, Cr(Ⅲ)
ABSTRACT
It is emergent to develop a green waste water adsorbent with high
efficiency. Therefore, a type of low-cost, green and environmentally friendly
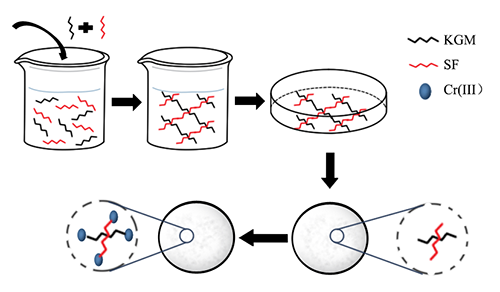
konjac glucomannan (KGM)-silk fibroin (SF) composite aerogels were compounded
via simple chemical grafting and vacuum freeze drying, and a study on its
adsorption capacity was also conducted. The characterizations of FT-IR, SEM,
XRD and DSC indicate that the modified aerogels show a porous network space
structure and there is a strong hydrogen bond effect between the KGM and SF
molecules, which improves the density, compressive strength and thermal
stability of aerogel materials. The adsorption experiments show that KGM-SF
aerogels can effectively adsorb the water pollutants
Cr(Ⅲ) with a maximal adsorption capacity of 82 mg·g-1. In addition,
the adsorption isotherm and dynamic model analysis are used to elaborate the
adsorption mechanism of KGM-SF aerogels and explain that the composite aerogels
can be single molecule chemisorption. KGM-SF aerogels have potential adsorption capacity.